Arduino Tutorial: KY-015 Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module
Abstract
Learn how to use the KY-015 Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module with Arduino. This module typically integrates a DHT11 or similar sensor, which uses a single-wire digital protocol to transmit two measurements: air temperature and relative humidity. Unlike simple analog sensors, this requires the use of a specialized software library to handle the sensor’s complex timing and data packet transmission.
1. Introduction
The KY-015 is an essential environmental monitoring component. It relies on a combination of a thermistor and a capacitive sensor to measure:
- Relative Humidity (RH): The amount of water vapor in the air, expressed as a percentage.
- Air Temperature: Measured in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
The data is transmitted over a single wire in a 40-bit packet. The Arduino must precisely time the duration of HIGH and LOW signals to decode this data, which is why a dedicated library is required.
In this episode, you’ll learn:
- The concept of a single-wire digital protocol.
- How to install and use a DHT sensor library.
- How to read and interpret both temperature and humidity
- How to detect common sensor reading errors.
This project provides a reliable method for real-time environmental data acquisition.
2. Prerequisites
Make sure you have:
- An Arduino Uno or compatible board.
- One KY-015 Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module (or equivalent DHT sensor).
- Jumper Wires.
- Arduino IDE
- Library Installation: You must install the Adafruit DHT Unified Sensor Library and the DHT sensor library (by Adafruit) via the Arduino Library Manager.
3. Wiring and Setup for Arduino
The KY-015 module has three pins and requires one digital input pin.
Step 1 – Identify Pins
The module typically has three pins: Signal (S or OUT), VCC (+), and GND (− or GND).
Step 2 – Connect the Module
Wire the module to the Arduino as follows:
- Connect the GND pin of the KY-015 to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the VCC pin of the KY-015 to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the S / Signal pin of the KY-015 to Arduino Digital Pin 2.
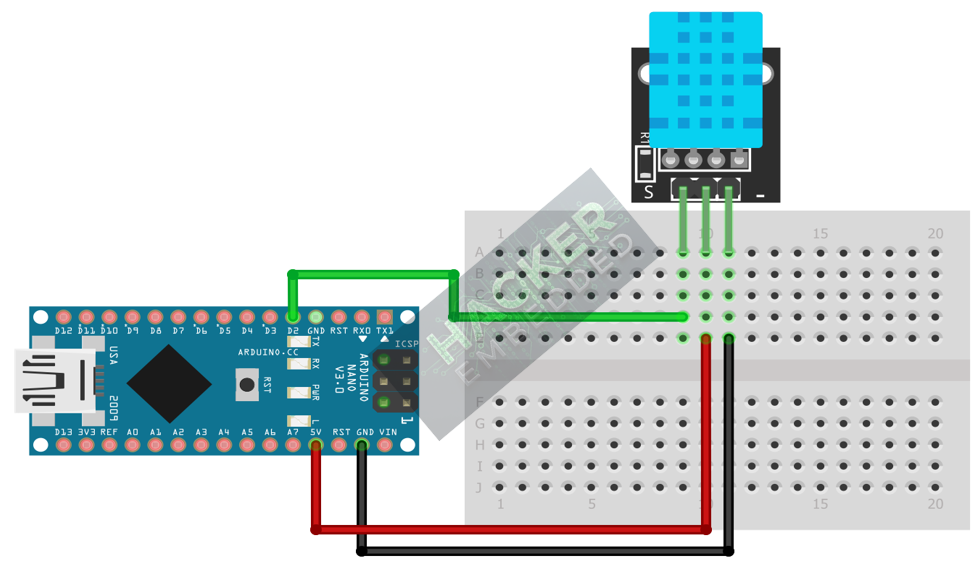
This image was created with Fritzing
Step 3 – Define Sensor Type
We will define the sensor type for the library. We will assume the common DHT11 sensor type.
4. Writing Digital Protocol Code
We will use the Adafruit DHT library to simplify the complex communication and read the environmental data.
Open main.ino and implement the following code.
#include "DHT.h" // Include the required library
// 1. Define Hardware Pin and Sensor Type
#define DHTPIN 2 // Digital pin connected to the DHT sensor
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // Define the sensor type (e.g., DHT11, DHT22)
// 2. Initialize DHT Sensor
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("KY-015 DHT Sensor Test Ready!");
dht.begin();
}
void loop() {
// DHT sensors are slow. Only read once every 2 seconds (minimum delay).
delay(2000);
// --- 1. Read Humidity ---
float h = dht.readHumidity();
// --- 2. Read Temperature (Celsius) ---
float t = dht.readTemperature();
// --- 3. Check for Reading Failure ---
if (isnan(h) || isnan(t)) {
Serial.println("!!! Failed to read from DHT sensor! Check wiring.");
return;
}
// --- 4. Convert to Fahrenheit (Optional) ---
float f = t * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32.0;
// --- 5. Calculate Heat Index (Optional) ---
float hi = dht.computeHeatIndex(f, h);
// --- 6. Print Results ---
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(h);
Serial.print(" %\t");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(t);
Serial.print(" C / ");
Serial.print(f);
Serial.print(" F\t");
Serial.print("Heat Index: ");
Serial.print(hi);
Serial.println(" F");
}
Code Explanation
- #include “DHT.h”: Imports the necessary code for the single-wire communication protocol.
- readHumidity() / dht.readTemperature(): These library functions handle the complex timing, bit reading, and checksum verification of the sensor’s 40-bit data packet, returning the measured value.
- isnan() Check: DHT sensors are prone to errors. If the library fails to get a valid reading (due to timing issues or bad data), it returns “Not a Number” (NaN), which the code checks for to prevent printing garbage data.
5. Uploading and Testing the Project
Step 1 – Build & Upload
Complete the standard build and upload process.
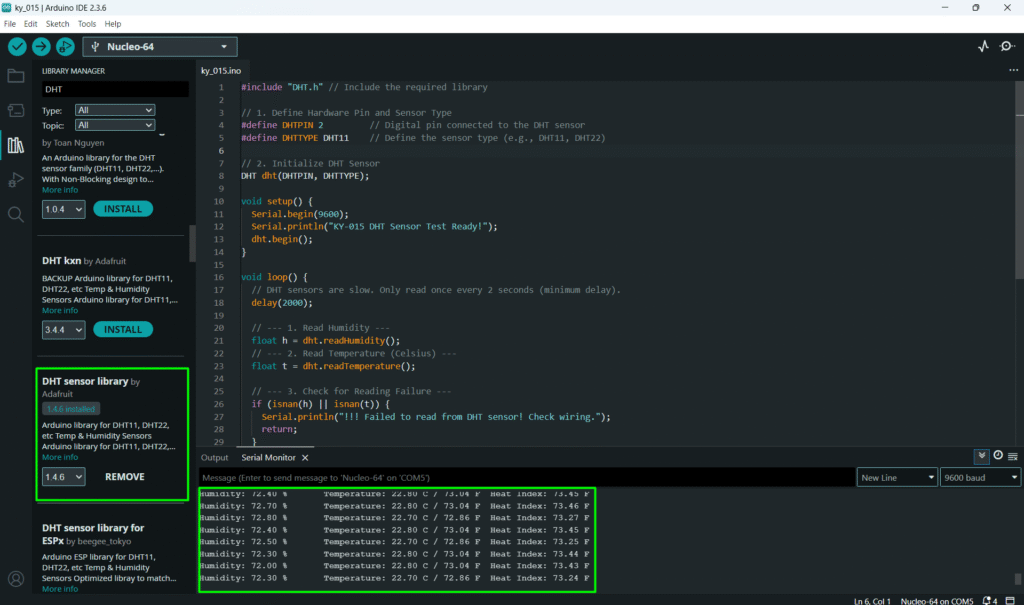
Step 2 – Test
- Open the Serial Monitor (Tools > Serial Monitor).
- After a brief initialization period, readings should start appearing every 2 seconds.
- Test Environment: Place your finger on the sensor or breathe on it. The Humidity reading should increase rapidly, and the Temperature reading should show a small, gradual rise.
6. Hands-On Lab Recap
You’ve learned:
- The difference between simple analog/digital sensing and a single-wire digital protocol.
- The necessity of using a software library to handle complex sensor communication.
- How to read and print temperature, humidity, and heat index.
This concludes the comprehensive series on fundamental KY-series modules.
7. Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Error: Failed to read from DHT sensor! | Timing error or bad wiring. | Check the VCC, GND, and Signal (S) wire to Pin 2. Increase the delay() to 3s or more to give the sensor time to stabilize. |
| Code doesn't compile (Header file not found). | Missing Libraries. | Ensure you have installed both the Adafruit DHT Unified Sensor Library and the DHT sensor library (by Adafruit). |
| Temperature is stuck at a fixed value (0 or 255). | Wrong Sensor Type defined. | If your module uses a DHT22, change #define DHTTYPE DHT11 to #define DHTTYPE DHT22 and re-upload. |
| Temperature is reasonable, but Humidity is 0 or 100%. | Sensor limitation or damage. | DHT11 is less precise. Try to use a small external pull-up resistor (e.g., 10kΩ) on the data line if readings are erratic. |