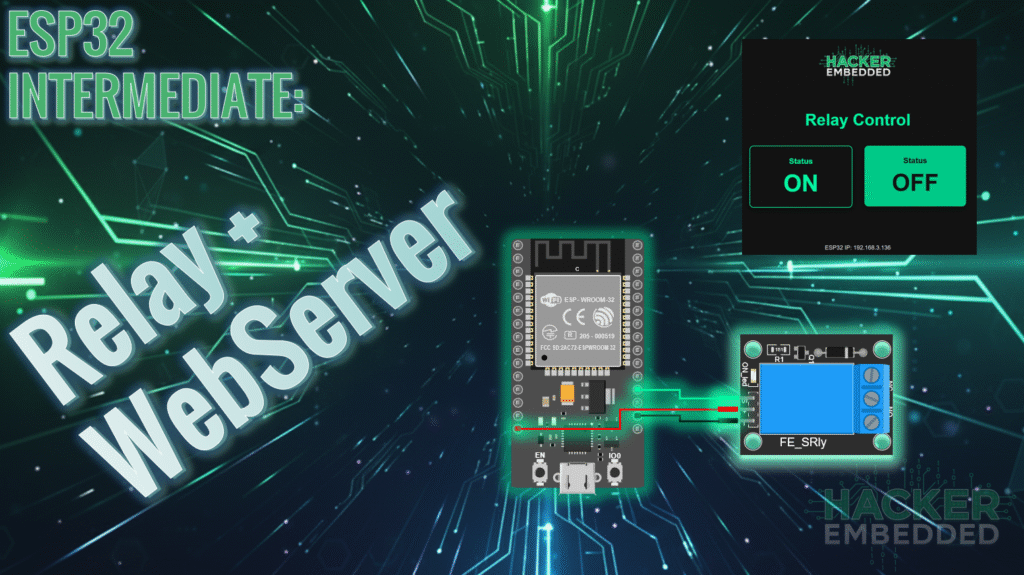
ESP32 Tutorial: Web Server Control for KY-019 Relay Module
Abstract
This tutorial covers interfacing the KY-019 5V Relay Module with the ESP32 and creating a simple web server dashboard to remotely control the relay’s state (ON/OFF). The ESP32 will host a web page with buttons that send requests to change the state of the relay, demonstrating remote control of high-power devices using the ESP32’s Wi-Fi capability.
1. Introduction to Remote Power Control
One of the most valuable applications of the ESP32 in the Internet of Things (IoT) is its ability to remotely control physical devices. This is achieved by using a Relay Module, which acts as a robust, electrically isolated switch capable of controlling high-voltage or high-current loads (like lights or appliances) that the low-power microcontroller cannot directly handle.
This tutorial focuses on interfacing the common KY-019 5V Relay Module with the ESP32 and building a simple, intuitive web server dashboard for remote control. This project demonstrates several intermediate concepts:
Active-LOW Logic: Understanding that many common relay modules, including the KY-019, are Active-LOW, meaning they switch ON when the control pin is set to
LOW(GND) and OFF when set toHIGH(3.3V).Web Control: Hosting a dashboard that uses simple HTTP GET requests (via on-screen buttons/links) to trigger physical actions.
Best Practices: Highlighting the crucial need for separate power for the relay coil to protect the ESP32 and ensure reliable switching.
By the end of this guide, you will have a functional system that allows you to control a physical switch from any web browser on your local Wi-Fi network.
2. Prerequisites and Wiring
2.1 Hardware
- ESP32 Dev Board
- KY-019 5V Relay Module
- Jumper Wires
- A separate power supply for the relay (optional, but recommended), as the ESP32’s 3.3V logic may not reliably drive the 5V relay coil, and drawing high current from the ESP32’s 3.3V line is discouraged.
2.2 ESP32-to-KY-019 Wiring
The KY-019 is an active-LOW relay module (it energizes the coil when the input is LOW/GND).
ESP32 Pin | KY-019 Pin | Notes |
GPIO 2 | IN (Signal) | The control pin from the ESP32. |
5V/VCC | VCC | Power for the relay coil (usually 5V). Connect to the ESP32’s 5V pin or a separate 5V supply. |
GND | GND | Ground connection. |
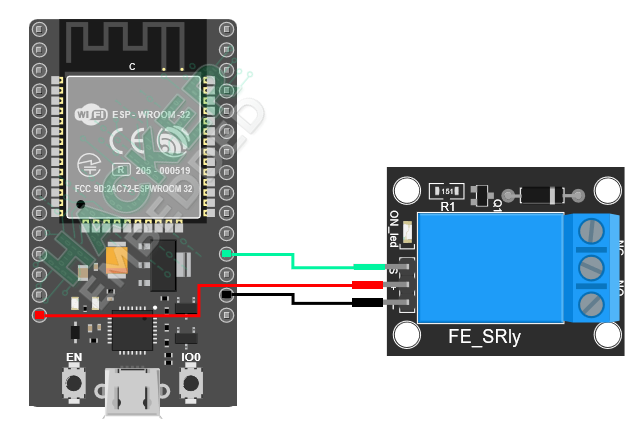
Important Note on Relay Power: For reliable operation, especially when switching a load, it is best practice to power the relay coil (KY-019 VCC/GND) from an external 5V supply rather than the ESP32’s 5V pin, which is typically derived from the USB port and may not provide enough stable current. The GPIO 2 signal line connects the ESP32’s logic to the relay’s optoisolator.
3. The ESP32 Arduino Sketch
The code initializes the Wi-Fi connection, sets the relay pin as an output, and defines web server handlers to process requests for turning the relay ON or OFF.
3.1 Libraries and Global Variables
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WebServer.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "YOUR_WIFI_SSID";
const char* password = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
// Pin connected to the Relay's IN terminal (GPIO 2)
const int RELAY_PIN = 2;
// The KY-019 is typically Active-LOW, meaning LOW = ON
const int RELAY_ON = LOW;
const int RELAY_OFF = HIGH;
// Global state variable
bool relayState = false;
WebServer server(80);
3.2 Web Handlers and Control Functions
We define three handlers: one for the root page (/), and two specific handlers to change the state (/on and /off).
// Function to physically set the relay state
void setRelay(bool state) {
relayState = state;
// Write the corresponding logic level to the pin:
// state=true (ON) -> RELAY_ON (LOW)
// state=false (OFF) -> RELAY_OFF (HIGH)
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, state ? RELAY_ON : RELAY_OFF);
// Print the logical state (what was commanded)
Serial.print("Relay commanded to: ");
Serial.println(state ? "OFF" : "ON");
// Print the actual pin level for deeper debugging
Serial.print("Pin state is: ");
Serial.println(digitalRead(RELAY_PIN) == HIGH ? "HIGH" : "LOW");
// After action, redirect back to the main dashboard
server.sendHeader("Location", "/");
server.send(303); // HTTP 303: See Other (redirect)
}
// Handler for turning the relay ON
void handleOn() {
setRelay(false);
}
// Handler for turning the relay OFF
void handleOff() {
setRelay(true);
}
// Handler for the root web page (dashboard)
void handleRoot() {
server.send(200, "text/html", getHtmlPage());
}
3.3 HTML Generation
The HTML page displays the current status and provides distinct buttons/links to change the state.
String getHtmlPage() {
// Determine the current state string and corresponding colors
String statusTextOn = "ON";
String statusTextOff = "OFF";
String onBoxColor = "#00f5a0"; // Your highlight color for ON
String offBoxColor = "#00c987"; // Dark green for OFF
// Determine if ON or OFF box should be highlighted
String onBoxStyle = relayState ? "background-color: " + onBoxColor + "; color: #121212;" : "border: 2px solid " + onBoxColor + "; color: " + onBoxColor + ";";
String offBoxStyle = !relayState ? "background-color: " + offBoxColor + "; color: #121212;" : "border: 2px solid " + offBoxColor + "; color: " + offBoxColor + ";";
String html = R"rawliteral(
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="2">
<style>
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* GLOBAL STYLES & COLOR PALETTE */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
:root {
--color-primary: #00f5a0; /* Bright Green/Teal for ON */
--color-off-dark-green: #00c987; /* Darker Green for OFF */
--color-background: #121212; /* Dark/Black */
--color-text-light: #d1d5db; /* Light gray for general text */
--color-text-dark: #121212; /* Dark text for inside bright boxes */
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 0;
padding-top: 50px; /* Space for logo/title */
background-color: var(--color-background);
color: var(--color-text-light);
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
min-height: 100vh;
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* LOGO & TITLE */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.logo {
width: 200px; /* Adjust size as needed */
height: auto;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
h1 {
color: var(--color-primary); /* Use primary color for main title */
font-size: 2.5em;
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* STATUS BOXES (ON/OFF) */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.status-grid {
display: flex;
gap: 30px; /* Space between the ON and OFF boxes */
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.status-box {
width: 250px; /* Fixed width for the boxes */
height: 150px; /* Fixed height for the boxes */
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 15px rgba(0,0,0,0.5); /* Stronger shadow for contrast */
font-size: 1.2em;
font-weight: bold;
transition: all 0.3s ease; /* Smooth transition for active state */
position: relative; /* Needed for .btn absolute positioning */
}
.status-value {
font-size: 3em; /* Larger font for ON/OFF text */
margin-top: 10px;
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* BUTTONS (LINKS) */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.btn {
text-decoration: none;
display: block; /* Make the whole box clickable */
cursor: pointer;
position: absolute; /* Position over the status box */
top: 0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0;
z-index: 1; /* Ensure it's clickable */
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FOOTER / IP INFO */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.footer-info {
margin-top: 50px;
color: var(--color-text-light); /* Light gray for secondary info */
font-size: 0.9em;
}
</style>
<title>Hacker Embedded Relay Control</title>
</head>
<body>
<img decoding="async" src="https://www.github.com/hackerembedded/STM32/blob/main/Logo%20Hacker%20Embedded.png?raw=true" alt="Hacker Embedded Logo" class="logo">
<h1>Relay Control</h1>
<div class="status-grid">
<div class="status-box" style="ON_BOX_STYLE;">
Status
<span class="status-value">ON</span>
<a href="/on" class="btn"></a>
</div>
<div class="status-box" style="OFF_BOX_STYLE;">
Status
<span class="status-value">OFF</span>
<a href="/off" class="btn"></a>
</div>
</div>
<p class="footer-info">ESP32 IP: IP_ADDRESS</p>
<p class="footer-info">Update Count: X seconds ago</p>
</body>
</html>
)rawliteral";
// Replace placeholders with current data
html.replace("ON_BOX_STYLE", onBoxStyle);
html.replace("OFF_BOX_STYLE", offBoxStyle);
html.replace("IP_ADDRESS", WiFi.localIP().toString());
// You'll need to dynamically update "X seconds ago" from your C++ code
html.replace("X", "XX"); // Placeholder for dynamic update count
return html;
}
3.4 Setup and Loop
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Set the relay pin as an output and ensure it starts in the OFF state
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, RELAY_OFF);
// Connect to Wi-Fi
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to WiFi...");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected.");
Serial.print("Web Server IP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// Setup Web Server Routes
server.on("/", handleRoot);
server.on("/on", handleOn);
server.on("/off", handleOff);
server.begin();
}
void loop() {
// Must continuously handle incoming web requests
server.handleClient();
}
4. Source Code
The entire code for an easier copy and paste:
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WebServer.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "SSID";
const char* password = "PASSWORD";
// Pin connected to the Relay's IN terminal (GPIO 2)
const int RELAY_PIN = 2;
// The KY-019 is typically Active-LOW, meaning LOW = ON
const int RELAY_ON = LOW;
const int RELAY_OFF = HIGH;
// Global state variable
bool relayState = false;
WebServer server(80);
// Function to physically set the relay state
void setRelay(bool state) {
relayState = state;
// Write the corresponding logic level to the pin:
// state=true (ON) -> RELAY_ON (LOW)
// state=false (OFF) -> RELAY_OFF (HIGH)
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, state ? RELAY_ON : RELAY_OFF);
// Print the logical state (what was commanded)
Serial.print("Relay commanded to: ");
Serial.println(state ? "OFF" : "ON");
// Print the actual pin level for deeper debugging
Serial.print("Pin state is: ");
Serial.println(digitalRead(RELAY_PIN) == HIGH ? "HIGH" : "LOW");
// After action, redirect back to the main dashboard
server.sendHeader("Location", "/");
server.send(303); // HTTP 303: See Other (redirect)
}
// Handler for turning the relay ON
void handleOn() {
setRelay(false);
}
// Handler for turning the relay OFF
void handleOff() {
setRelay(true);
}
// Handler for the root web page (dashboard)
void handleRoot() {
server.send(200, "text/html", getHtmlPage());
}
String getHtmlPage() {
// Determine the current state string and corresponding colors
String statusTextOn = "ON";
String statusTextOff = "OFF";
String onBoxColor = "#00f5a0"; // Your highlight color for ON
String offBoxColor = "#00c987"; // Dark green for OFF
// Determine if ON or OFF box should be highlighted
String onBoxStyle = relayState ? "background-color: " + onBoxColor + "; color: #121212;" : "border: 2px solid " + onBoxColor + "; color: " + onBoxColor + ";";
String offBoxStyle = !relayState ? "background-color: " + offBoxColor + "; color: #121212;" : "border: 2px solid " + offBoxColor + "; color: " + offBoxColor + ";";
String html = R"rawliteral(
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="2">
<style>
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* GLOBAL STYLES & COLOR PALETTE */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
:root {
--color-primary: #00f5a0; /* Bright Green/Teal for ON */
--color-off-dark-green: #00c987; /* Darker Green for OFF */
--color-background: #121212; /* Dark/Black */
--color-text-light: #d1d5db; /* Light gray for general text */
--color-text-dark: #121212; /* Dark text for inside bright boxes */
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 0;
padding-top: 50px; /* Space for logo/title */
background-color: var(--color-background);
color: var(--color-text-light);
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
min-height: 100vh;
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* LOGO & TITLE */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.logo {
width: 200px; /* Adjust size as needed */
height: auto;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
h1 {
color: var(--color-primary); /* Use primary color for main title */
font-size: 2.5em;
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* STATUS BOXES (ON/OFF) */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.status-grid {
display: flex;
gap: 30px; /* Space between the ON and OFF boxes */
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.status-box {
width: 250px; /* Fixed width for the boxes */
height: 150px; /* Fixed height for the boxes */
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 15px rgba(0,0,0,0.5); /* Stronger shadow for contrast */
font-size: 1.2em;
font-weight: bold;
transition: all 0.3s ease; /* Smooth transition for active state */
position: relative; /* Needed for .btn absolute positioning */
}
.status-value {
font-size: 3em; /* Larger font for ON/OFF text */
margin-top: 10px;
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* BUTTONS (LINKS) */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.btn {
text-decoration: none;
display: block; /* Make the whole box clickable */
cursor: pointer;
position: absolute; /* Position over the status box */
top: 0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0;
z-index: 1; /* Ensure it's clickable */
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FOOTER / IP INFO */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
.footer-info {
margin-top: 50px;
color: var(--color-text-light); /* Light gray for secondary info */
font-size: 0.9em;
}
</style>
<title>Hacker Embedded Relay Control</title>
</head>
<body>
<img decoding="async" src="https://www.github.com/hackerembedded/STM32/blob/main/Logo%20Hacker%20Embedded.png?raw=true" alt="Hacker Embedded Logo" class="logo">
<h1>Relay Control</h1>
<div class="status-grid">
<div class="status-box" style="ON_BOX_STYLE;">
Status
<span class="status-value">ON</span>
<a href="/on" class="btn"></a>
</div>
<div class="status-box" style="OFF_BOX_STYLE;">
Status
<span class="status-value">OFF</span>
<a href="/off" class="btn"></a>
</div>
</div>
<p class="footer-info">ESP32 IP: IP_ADDRESS</p>
<p class="footer-info">Update Count: X seconds ago</p>
</body>
</html>
)rawliteral";
// Replace placeholders with current data
html.replace("ON_BOX_STYLE", onBoxStyle);
html.replace("OFF_BOX_STYLE", offBoxStyle);
html.replace("IP_ADDRESS", WiFi.localIP().toString());
// You'll need to dynamically update "X seconds ago" from your C++ code
html.replace("X", "XX"); // Placeholder for dynamic update count
return html;
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Set the relay pin as an output and ensure it starts in the OFF state
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, RELAY_OFF);
// Connect to Wi-Fi
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to WiFi...");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected.");
Serial.print("Web Server IP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// Setup Web Server Routes
server.on("/", handleRoot);
server.on("/on", handleOn);
server.on("/off", handleOff);
server.begin();
}
void loop() {
// Must continuously handle incoming web requests
server.handleClient();
}
4.1 Code Explanation and Logic Breakdown
The code centers on managing the Active-LOW logic of the relay and setting up the web server routes to map URL requests to physical pin changes.
4.1.1 Constants and State Management
Logic Mapping: The critical step is defining constants that map the desired logical state (ON/OFF) to the physical voltage level required by the KY-019 relay:
const int RELAY_ON = LOW; // Active-LOW
const int RELAY_OFF = HIGH;
relayState: A globalboolvariable is used to track the logical state (truefor ON,falsefor OFF), which is distinct from the physical pin voltage. This simplifies the HTML generation logic.
4.1.2 The Control Function (setRelay)
This single function handles the core action: writing the correct voltage to the GPIO pin and managing the web flow.
void setRelay(bool state) {
relayState = state;
// Ternary operator: if state is true (ON), use RELAY_ON (LOW), else RELAY_OFF (HIGH)
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, state ? RELAY_ON : RELAY_OFF);
// Redirect back to the dashboard after the action
server.sendHeader("Location", "/");
server.send(303); // HTTP 303: See Other
}
- Pin Control: The function uses a ternary operator to choose between
RELAY_ON(LOW) andRELAY_OFF(HIGH) based on the commandedstate. - Redirection (
server.send(303)): After successfully changing the relay state, the ESP32 sends an HTTP 303 (See Other) response with aLocationheader pointing back to the root page (/). This forces the browser to immediately refresh, loading the updated status dashboard without requiring the user to navigate manually.
4.1.3 Web Server Handlers
Three routes are defined in setup() to handle the web interaction:
/(Root): Handled byhandleRoot(), which serves the dynamic HTML dashboard (getHtmlPage())./on: Handled byhandleOn(), which callssetRelay(true)(logically ON)./off: Handled byhandleOff(), which callssetRelay(false)(logically OFF).
4.1.4 HTML Dashboard Generation
The getHtmlPage() function dynamically creates the webpage based on the global relayState.
Dynamic Styling: The function checks
relayStateto decide which status box (ONorOFF) should receive the highlighted style. This is achieved by substituting the CSS style strings (ON_BOX_STYLE,OFF_BOX_STYLE) right before the HTML is sent to the browser.Hyperlinks: The buttons in the HTML are simple hyperlinks (
<a href="/on" class="btn"></a>). Clicking a button sends a simple HTTP GET request to the corresponding endpoint (/onor/off), which triggers thesetRelayfunction and the subsequent redirection.
4.1.5 Setup and Loop
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT): Sets the control pin and immediately writesRELAY_OFF(HIGH) to ensure the relay starts in a known, safe OFF state upon boot.loop(): Theserver.handleClient()call is essential. It continuously monitors the network for incoming HTTP requests and directs them to the appropriate handler functions.
5. Hands-On Lab Recap
You have successfully established remote control over a physical switch using the ESP32:
- The KY-019 Relay Module is connected to a standard GPIO pin (GPIO 2) and controlled using the Active-LOW
- The ESP32 web server hosts a simple dashboard.
- Separate HTTP endpoints (/on and /off) are used to trigger the relay state change.
- After changing the state, the setRelay function uses sendHeader(“Location”, “/”) and server.send(303) to redirect the browser back to the updated dashboard automatically.
- Use the terminal to identify the IP and type it in the browser:

- Best Practice: Always use an external power supply for the relay coil, only connecting the ESP32’s GPIO 2 to the relay’s IN pin for logic control.