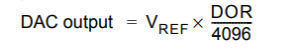STM32 HAL Tutorial: Generating Analog Signals from Digital Data
Abstract
Learn how to configure and use the STM32 DAC with HAL and CubeMX. Step-by-step guide for analog signal generation, waveform output, and peripheral interfacing.
1. Introduction
The DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter) on STM32 allows you to generate analog voltages from digital values.
Applications include:
- Audio signal generation
- Analog sensor simulation
- Voltage reference for other peripherals
- Waveform generation (sine, triangle, PWM smoothing)
By the end of this episode, you’ll be able to:
- Configure DAC using CubeMX and HAL
- Output constant and variable voltages
- Generate simple waveforms using timers or DMA
2. Prerequisites
- STM32 board with DAC peripheral (e.g., STM32G0, STM32G4, STM32H7)
- STM32CubeIDE installed
- Basic knowledge of HAL and GPIO
3. DAC Basics
- Converts digital value (e.g., 12-bit number) to analog voltage
- Output voltage formula:
- Can operate in normal mode or triggered mode (timer or software)
- Supports DMA for waveform generation
4. CubeMX Configuration
- Enable DAC peripheral
- Select DAC channel(s)
- Configure trigger (software, timer, or external)
- Enable DMA if waveform output is needed
- Generate initialization code
5. HAL Example: DAC Initialization
DAC_HandleTypeDef hdac1;
void MX_DAC1_Init(void)
{
DAC_ChannelConfTypeDef sConfig = {0};
hdac1.Instance = DAC1;
HAL_DAC_Init(&hdac1);
sConfig.DAC_Trigger = DAC_TRIGGER_NONE;
sConfig.DAC_OutputBuffer = DAC_OUTPUTBUFFER_ENABLE;
HAL_DAC_ConfigChannel(&hdac1, &sConfig, DAC_CHANNEL_1);
HAL_DAC_Start(&hdac1, DAC_CHANNEL_1);
}
6. Output a Constant Voltage
Converts digital value 2048 to ~1.65V if Vref = 3.3V
uint32_t value = 2048; // Mid-scale (Vref/2)
HAL_DAC_SetValue(&hdac1, DAC_CHANNEL_1, DAC_ALIGN_12B_R, value);
7. Generate a Waveform
Example: Sine wave using DMA and timer trigger
uint16_t sineWave[32] = {2048, 2447, 2831, 3185, 3495, ...}; // 12-bit values
HAL_DAC_Start_DMA(&hdac1, DAC_CHANNEL_1, (uint32_t*)sineWave, 32, DAC_ALIGN_12B_R);
Use timer to control update rate → frequency of waveform
8. Hands-On Lab Example
1. Initialize TIM6 to act as DAC’s trigger (100Hz)

2. Initialize DAC CHANNEL1
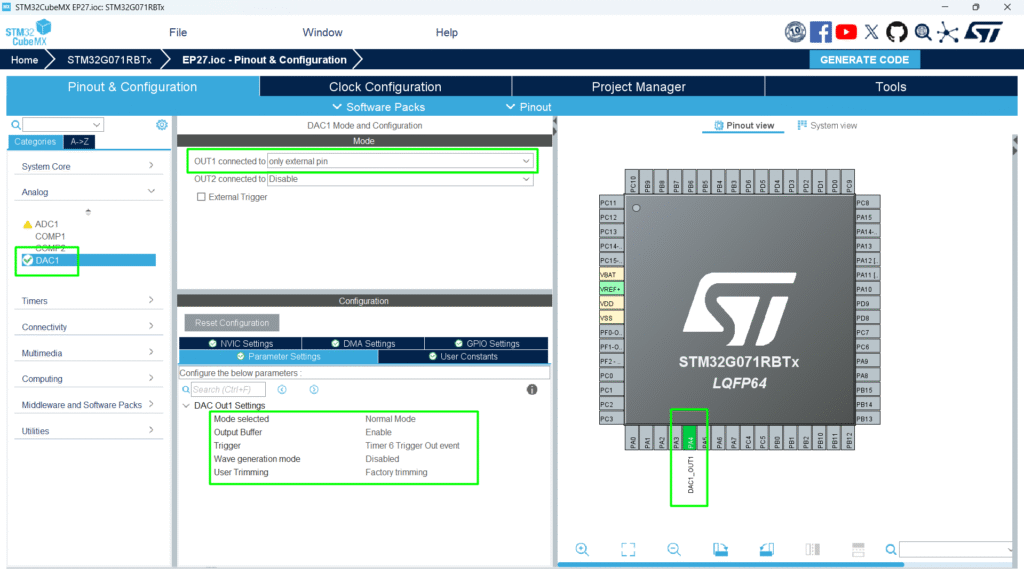
3. Configure the DMA
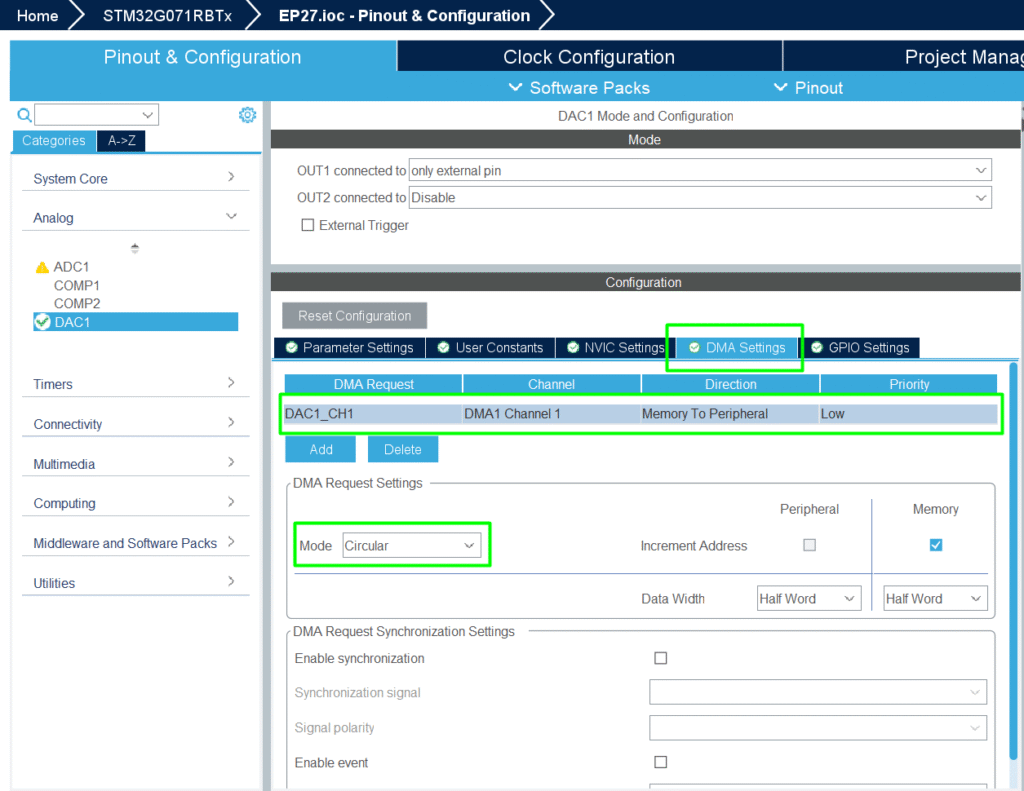
4. Create array of waveform samples (sine)
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
uint16_t u16DACBuff[32] = {
2048, 2447, 2831, 3185, 3495, 3751, 3940, 4056,
4095, 4056, 3940, 3751, 3495, 3185, 2831, 2447,
2048, 1649, 1265, 911, 601, 345, 156, 40,
1, 40, 156, 345, 601, 911, 1265, 1649
};
/* USER CODE END PV */
5. Use DMA + timer trigger to generate continuous waveform
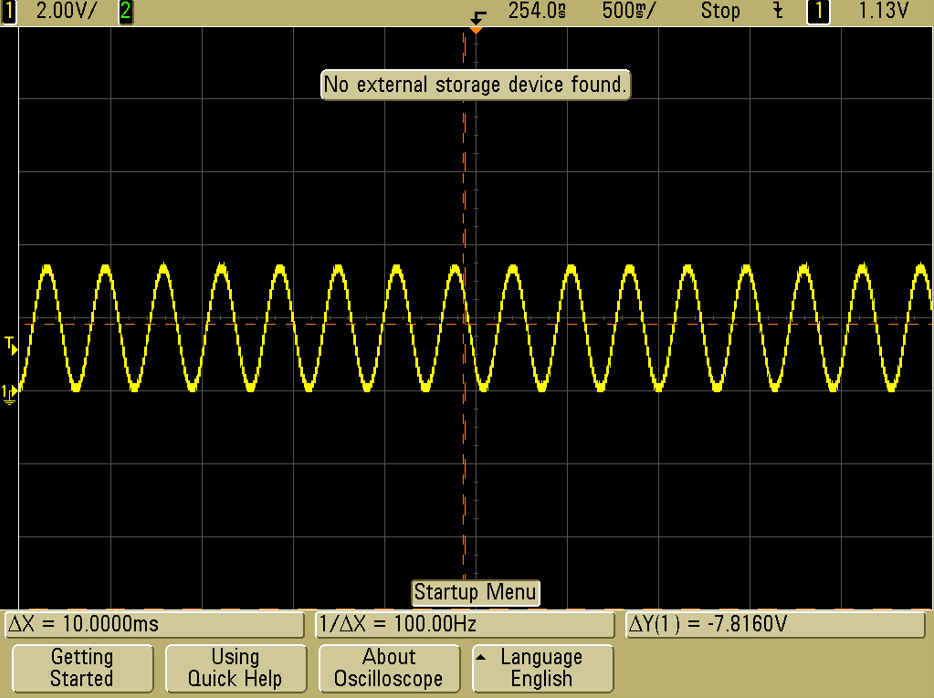
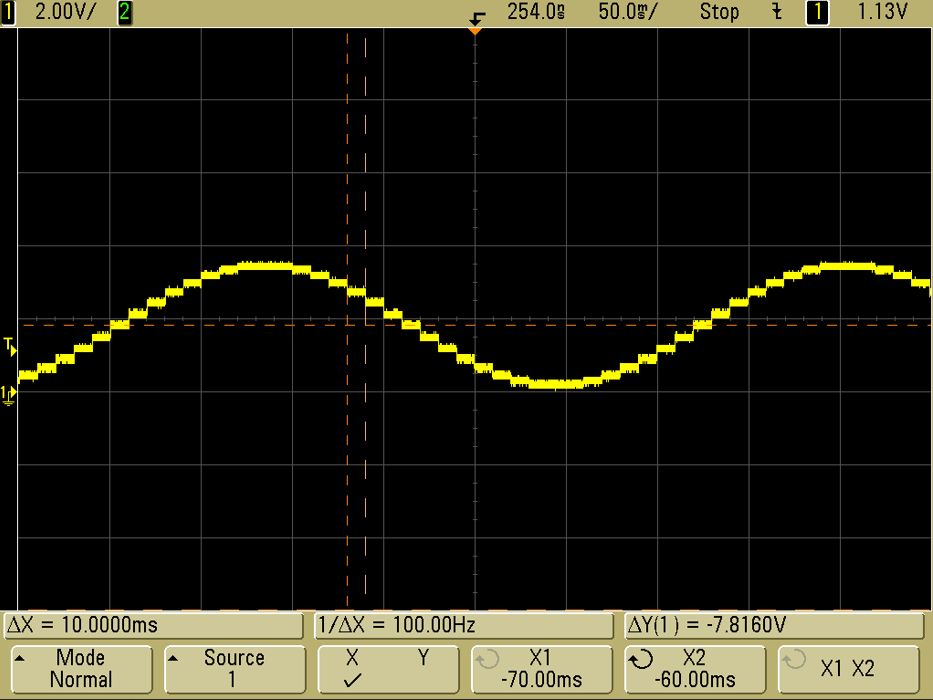
Tip: Use DAC + OpAmp for low-impedance analog signals suitable for sensors or actuators
9. Advantages of DAC
- Converts digital signals to analog with high precision
- Supports DMA and timers for continuous waveform generation
- Can interface with OpAmps, ADCs, or external circuits
- Essential for audio, control, and sensor applications