First STM32 Project: Blinking an LED Using HAL Drivers
Abstract
Learn how to create your first STM32 project using STM32CubeMX and HAL drivers. Step-by-step guide to configure GPIO pins and blink an LED using STM32CubeIDE.
1. Introduction
In the previous episode, we covered the basics of STM32CubeMX, HAL, and LL drivers.
Now, it’s time to build our first practical project:
Blink an LED using STM32 HAL drivers
This tutorial will guide you through:
- Creating a new project in STM32CubeIDE.
- Configuring GPIO pins using CubeMX.
- Writing a simple program to blink an LED.
- Compiling, flashing, and running the project on your STM32 board.
This is the “Hello World” of embedded systems development.

2. Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have:
✅ STM32CubeMX installed
✅ Your favorite IDE: STM32CubeIDE or VS Code installed
✅ An STM32 development board (e.g., Nucleo, Discovery, or Blue Pill)
✅ STM32CubeProgrammer (optional, for flashing via USB)
✅ USB cable to connect the board to your PC
Tip: If you haven’t installed STM32CubeMX nor know about it yet, check Episode 1.
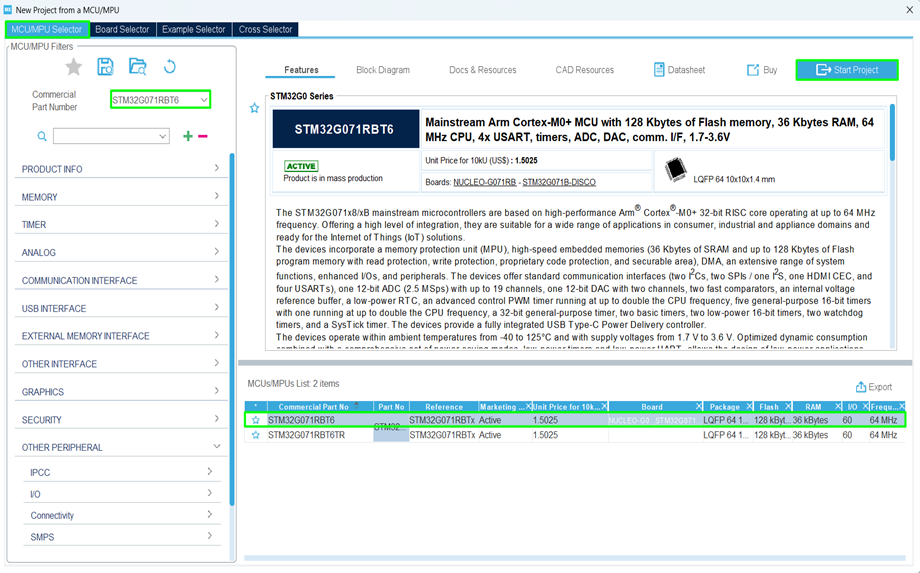
3. Creating a New STM32CubeMX Project
Step 1 – STM32CubeMX
- Launch STM32CubeMX.
- Click on [ACCESS TO MCU SELECTOR]
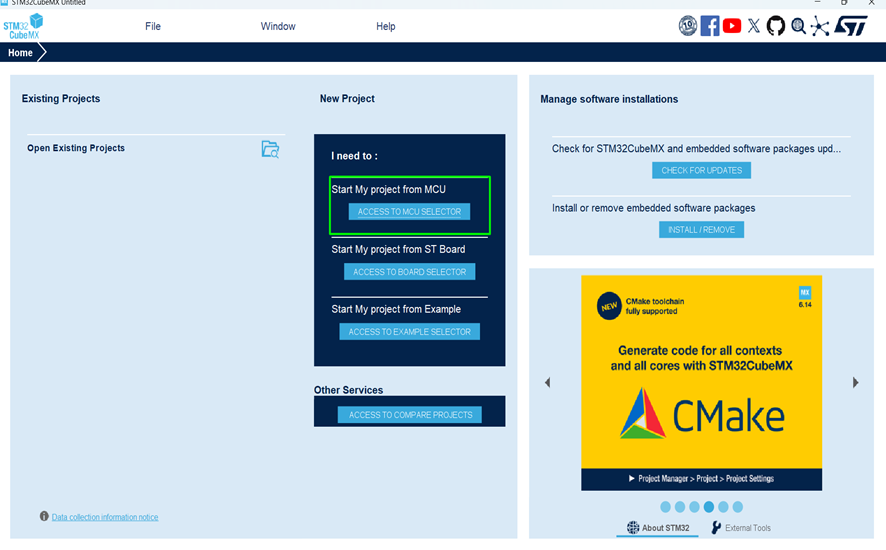
Step 2 – Select Your MCU or Board
You have two main options:
- By Board: Choose your development board (e.g., NUCLEO-G071RB).
- By MCU: Manually select your microcontroller (e.g., STM32G071RBT6).
Step 3 – Name Your Project
- Set a descriptive name, e.g., BlinkLED. The article will use EP2
- Leave the default toolchain as STM32CubeIDE.
- Click Finish.
4. Configuring GPIO in CubeMX
Once the project opens, you’ll see the STM32CubeMX graphical interface with your MCU pinout.
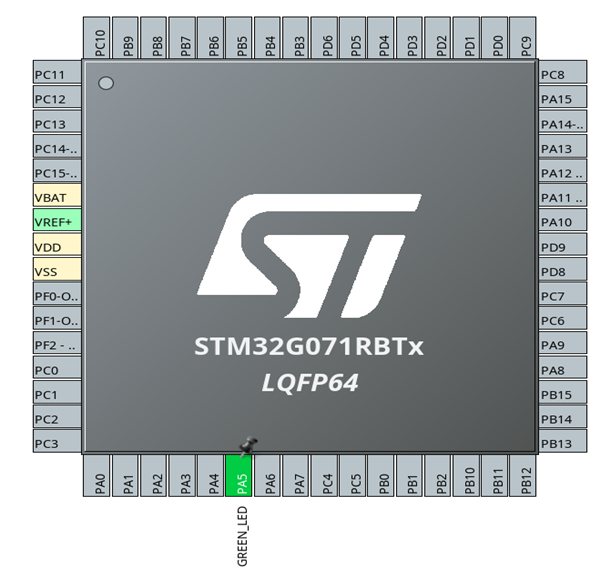
Step 1 – Enable LED Pin
- Locate the on-board LED pin (check your board manual).
- Example: On Nucleo boards, the user LED is usually PA5 and that is the case for the selected board: NUCLEO-G071RB
- Left Click on the pin and set its mode to GPIO_Output.
- Right Click on the pin and set its name as GREEN_LED
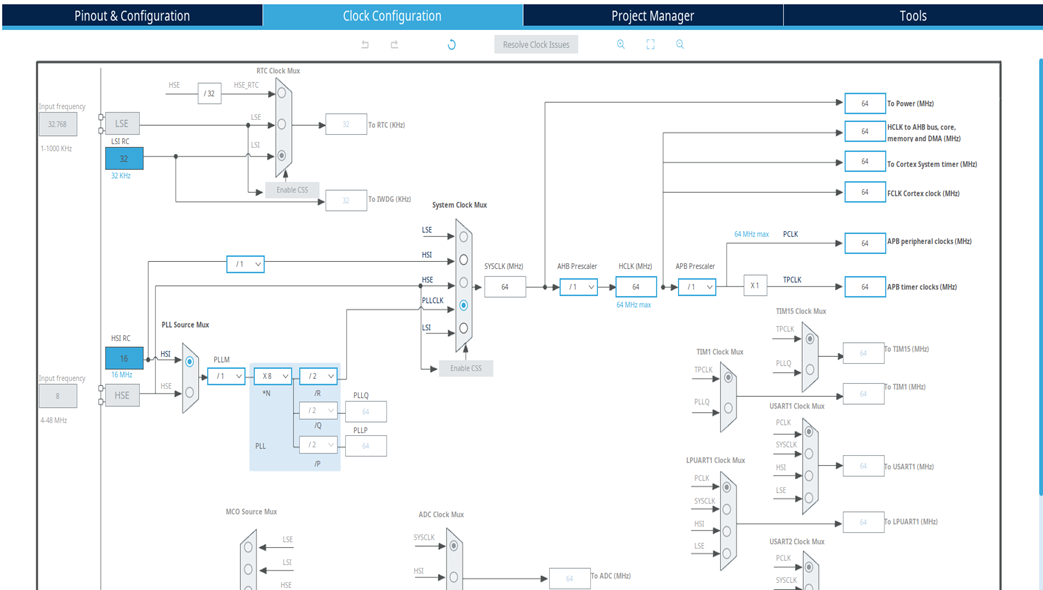
Step 2 – Configure System Clock (Optional)
- Go to the Clock Configuration
- Ensure the system clock is set to a stable and known frequency (e.g., 64 MHz for STM32G0 is the upper limit).
Step 3 – Generate Code
- Click Generate Code and Open the Project in STM32CubeIDE
- STM32CubeIDE will contain the project skeleton, including HAL initialization code.
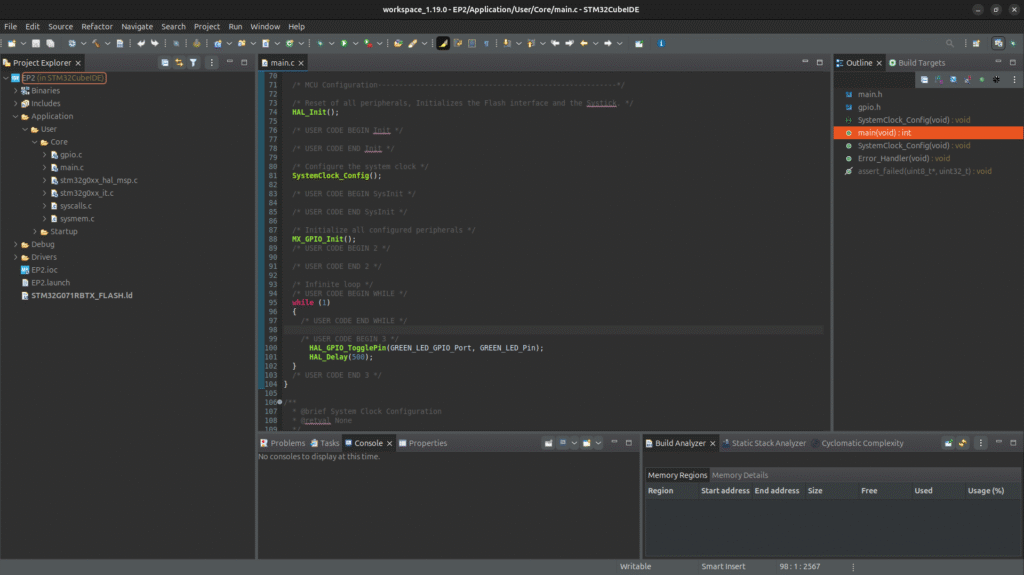
5. Writing the LED Blink Code
After CubeMX generates the project, open Core/Src/main.c.
Inside the while(1) loop, add the following code:
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GREEN_LED_GPIO_Port, GREEN_LED_Pin);
HAL_Delay(500);
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
Code Explanation
- HAL_GPIO_TogglePin() → Changes LED state (ON → OFF → ON).
- HAL_Delay(500) → Waits for 500 milliseconds before toggling again.
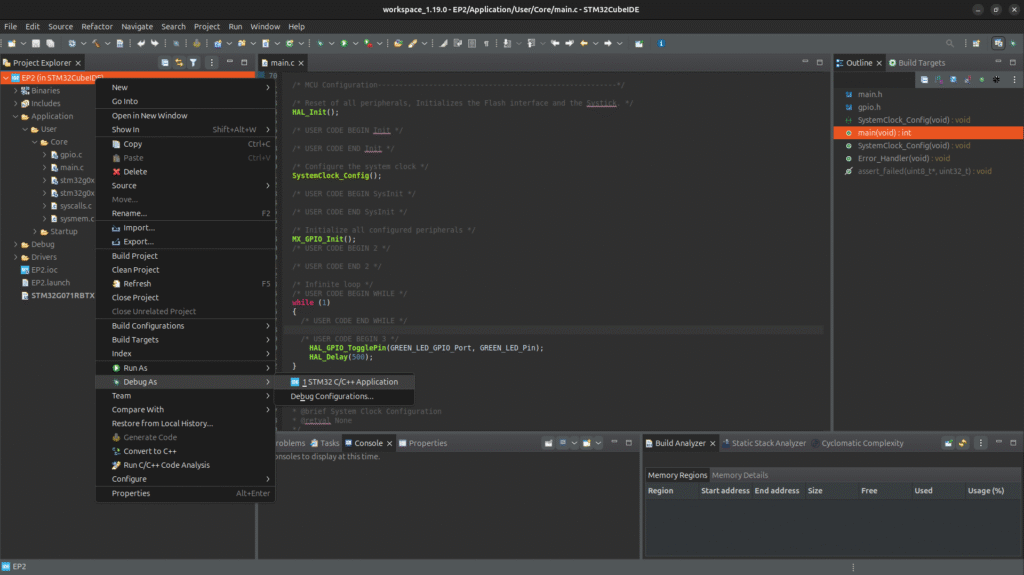
6. Compiling and Flashing the Code
Step 1 – Build the Project
- Click the hammer icon or press Ctrl + B.
Step 2 – Connect the Board
- Plug your STM32 board into your PC using a USB cable.
Step 3 – Flash the Code by entering in Debug Mode
- Right Click the Project name and locate the [Debug As] and select [STM32 C/C++ Application]. Default configuration will work.
- STM32CubeIDE will compile, flash, and run your code.
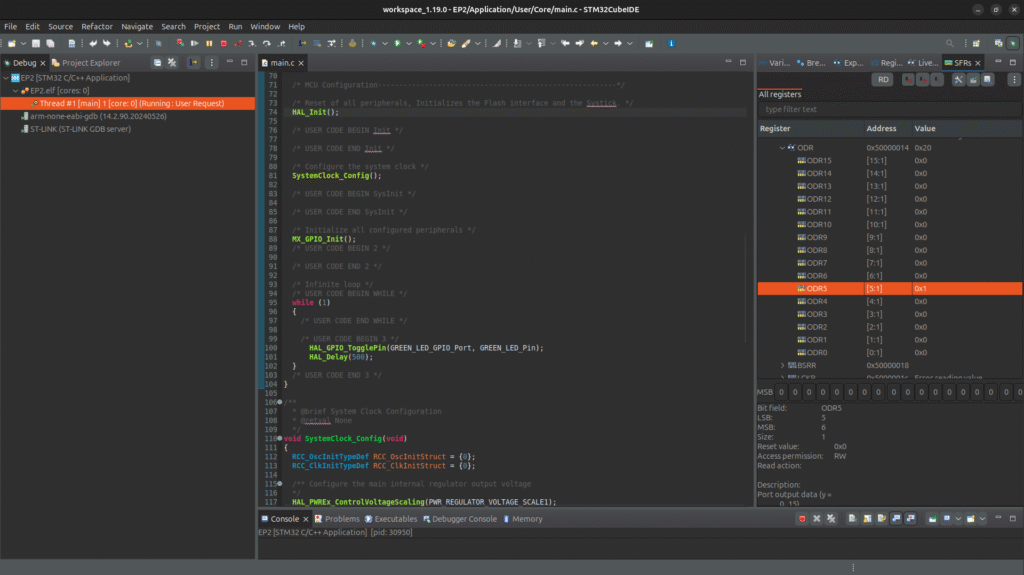
7. Testing the Project
If everything is configured correctly, the debug menu will appear and by clicking [Run]:
- The on-board LED should start blinking every 500ms.
- Its possible to check the GPIOA ODR register to see the change
- You can modify the delay value to change the blinking speed.
For example:
HAL_Delay(100); // Faster blink
HAL_Delay(1000); // Slower blink
8. Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| LED doesn’t blink | Wrong pin configured | Check board manual and CubeMX config |
| Compilation errors | Missing HAL drivers | Regenerate project and enable HAL |
| Board not detected | Board not detected | Missing USB driver |
| LED blinks too fast or slow | Clock misconfiguration | Check the system clock in CubeMX |
9. Hands-On Lab Recap
In this tutorial, you learned:
- How to create a new project in STM32CubeIDE.
- How to configure GPIO pins using CubeMX.
- How to write a simple LED blinking program.
- How to compile, flash, and test your project.
This completes the Hello World of STM32 development.
10. What’s Next
In Episode 3, we’ll go deeper into GPIO programming:
- Configuring input pins.
- Using push buttons to control LEDs.
- Handling debouncing with HAL.
Adding external interrupts for real-time response.