STM32 HAL Tutorial: Understanding MCU Reset Mechanisms and Triggering Resets
Abstract
Learn about STM32 reset sources, how the RCC handles resets, and how to trigger a software reset using HAL. Hands-on example included.
1. Introduction
STM32 MCUs have multiple reset sources, which ensure reliable operation under different conditions:
- Power-On Reset (POR/PDR) – MCU starts at power-up
- External reset (NRST pin) – Reset triggered by external circuit
- Software reset (SYSRESETREQ) – MCU can reset itself via code
- Watchdog reset – Independent (IWDG) or window (WWDG) watchdog triggers
- Low-power reset – Wake-up from standby or other low-power events
- Option byte loader
Understanding these reset sources is essential for:
- Debugging boot issues
- Designing robust firmware
- Implementing controlled resets for testing
2. Prerequisites
- STM32 board
- STM32CubeIDE or VS Code installed
- Knowledge of HAL and RCC
3. RCC and Reset Sources
The Reset and Clock Control (RCC) module manages:
- System clock sources
- Peripheral clocks
- Reset status flags
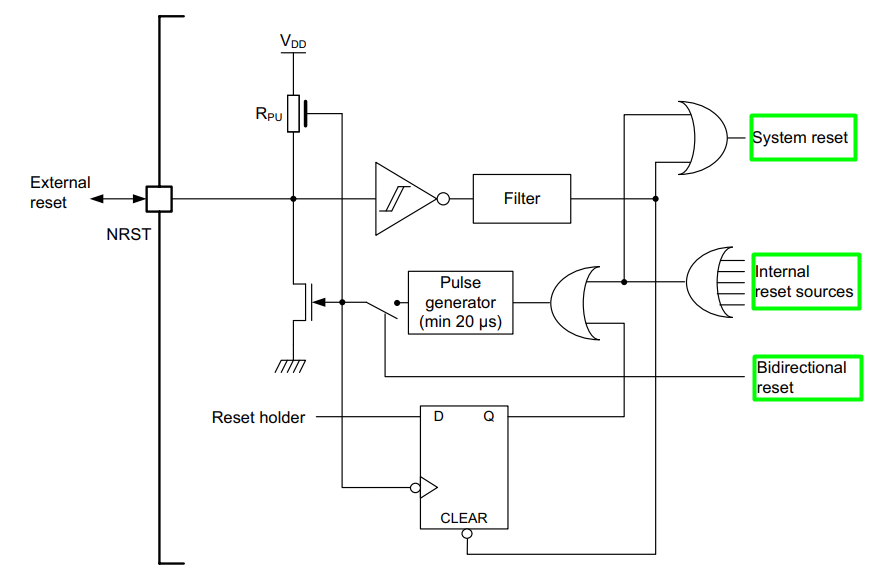
Reset flags indicate which reset occurred last, accessible via RCC_CSR register:
if (__HAL_RCC_GET_FLAG(RCC_FLAG_PINRST)) {
// Reset caused by NRST pin
}
if (__HAL_RCC_GET_FLAG(RCC_FLAG_PORRST)) {
// Reset caused by Power-On
}
if (__HAL_RCC_GET_FLAG(RCC_FLAG_SFTRST)) {
// Reset caused by software request
}
if (__HAL_RCC_GET_FLAG(RCC_FLAG_IWDGRST)) {
// Reset caused by Independent Watchdog
}
Flags are cleared using: __HAL_RCC_CLEAR_RESET_FLAGS();
4. Software Reset
STM32 can trigger a software reset using HAL:
void trigger_software_reset(void)
{
// Optional: perform pre-reset tasks
HAL_RCC_DeInit(); // Reset clocks to default
__HAL_RCC_CLEAR_RESET_FLAGS(); // Clear reset flags
NVIC_SystemReset(); // Trigger MCU reset
}
- NVIC_SystemReset() sets the SYSRESETREQ bit in SCB->AIRCR register
- MCU restarts as if powered-on
- Useful for:
- Firmware updates
- Recovering from error conditions
- Testing reset-handling code
5. Hands-On Lab Example
1. Create a new project configuring the UART and PC13
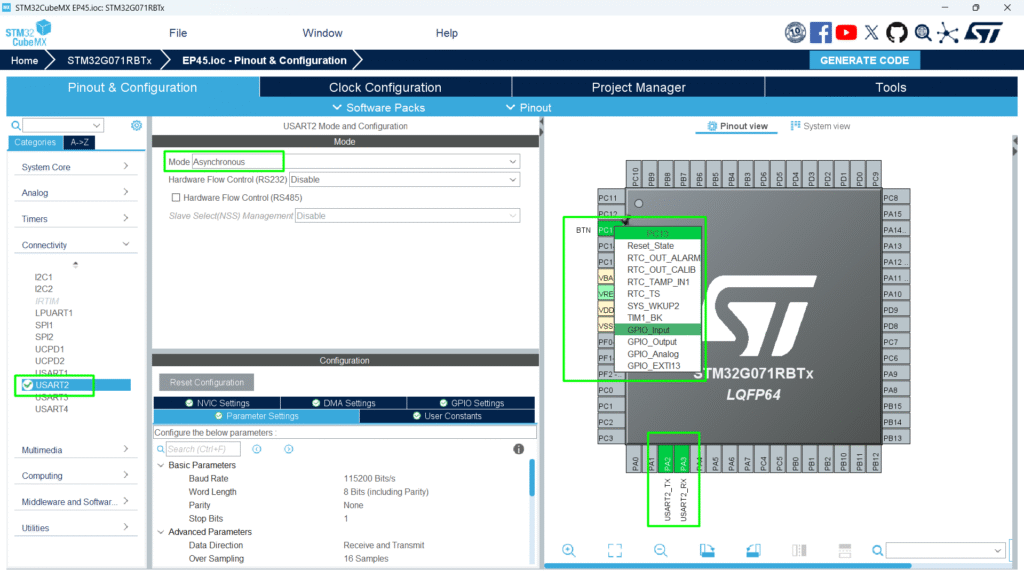
2. Check the last reset source:
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint32_t u32ResetCause;
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
u32ResetCause = __HAL_RCC_GET_FLAG(RCC_FLAG_SFTRST);
__HAL_RCC_CLEAR_RESET_FLAGS();
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
if(u32ResetCause)
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)"Software Reset\r\n", sizeof("Software Reset\r\n"), 1000);
}
/* USER CODE END 2 */
3. Trigger software reset when a button is pressed:
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(BTN_GPIO_Port, BTN_Pin) == GPIO_PIN_RESET)
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)"Button Pressed\r\n", sizeof("Button Pressed\r\n"), 1000);
NVIC_SystemReset(); //trigger MCU reset
}
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
4. Observe reset cause after reboot using LED or UART log
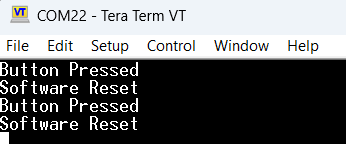
Example: LED blinks differently depending on reset source
6. Advantages
- Understanding RCC reset sources improves firmware reliability
- Software resets allow controlled MCU restart without power cycling
- Reset flags help diagnose boot or crash issues
- Crucial for low-power, fault-tolerant, and safety-critical applications
7. Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Software reset not triggered | NVIC_SystemReset not called or interrupts blocked | Ensure code reaches reset call |
| Reset flags not accurate | Flags not cleared after previous reset | Use __HAL_RCC_CLEAR_RESET_FLAGS() |
| MCU enters infinite reset loop | Reset triggered continuously | Add debounce or conditional reset logic |
| Watchdog resets immediately | IWDG or WWDG not refreshed | Feed watchdog if using it for normal operation |