STM32 HAL Tutorial: Understanding System Clocks and Outputting Them via MCO
Abstract
Learn how to configure the STM32 system clock tree and output clocks via MCO (Microcontroller Clock Output) using HAL. Hands-on demonstration included.
1. Introduction
The STM32 RCC (Reset and Clock Control) manages all MCU clocks:
- System Clock (SYSCLK) – main clock driving CPU
- AHB Clock (HCLK) – high-speed bus
- APB1 / APB2 clocks (PCLK1 / PCLK2) – peripheral clocks
- PLL (Phase-Locked Loop) – allows frequency multiplication
- MCO (Microcontroller Clock Output) – outputs internal clock to a pin for measurement
Using MCO, we can:
- Measure system clocks on an oscilloscope
- Verify PLL, HSE, HSI, or SYSCLK configuration
- Troubleshoot clock-related firmware issues
2. Prerequisites
- STM32 board
- STM32CubeIDE or VS Code installed
- Knowledge of HAL and RCC
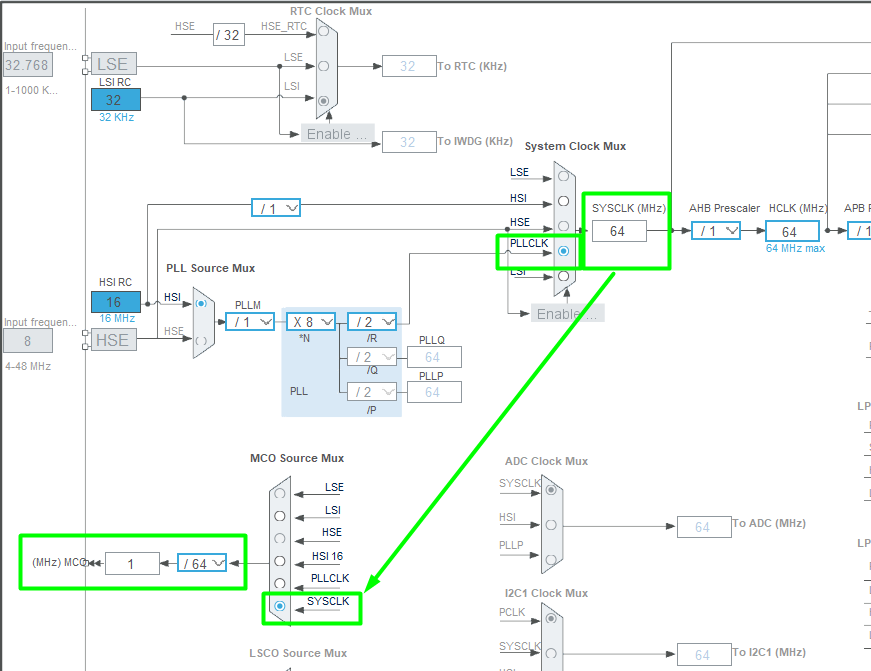
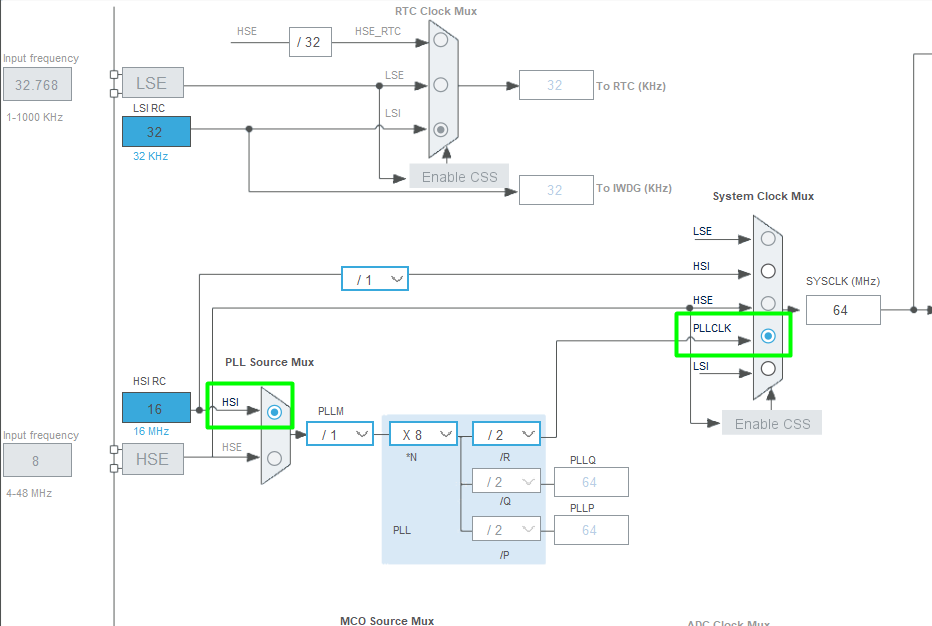
3. RCC Clock Tree Overview
- HSI (High-Speed Internal) – internal RC oscillator (~16 MHz)
- HSE (High-Speed External) – external crystal oscillator
- PLL – multiplies HSE/HSI to generate SYSCLK
- SYSCLK – system clock for CPU and AHB
- MCO1 / MCO2 pins – output selected clocks to a pin
Clock flow:
4. CubeMX Configuration
1. Configure system clock (HSE + PLL or HSI + PLL)
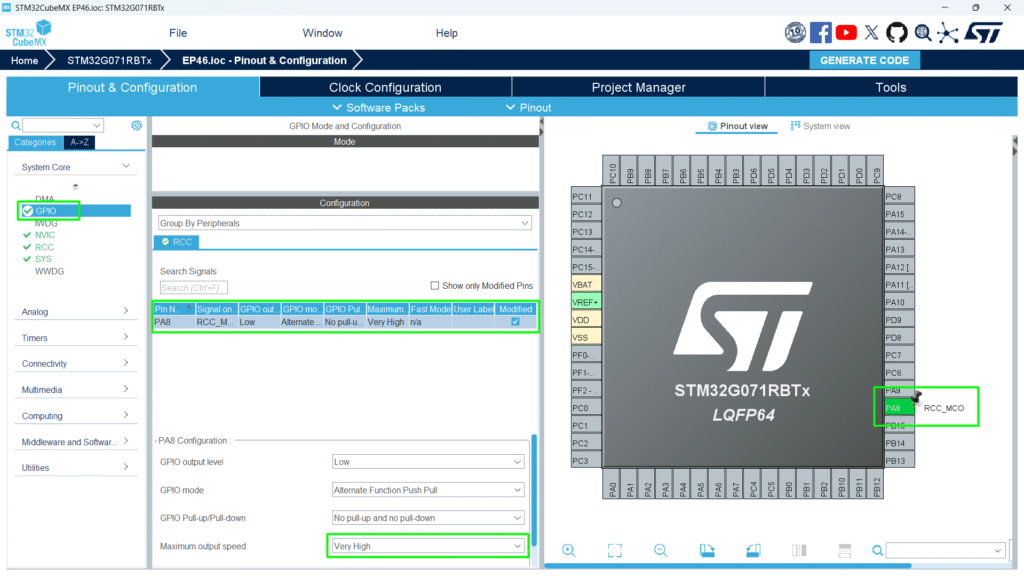
2. Enable MCO1 or MCO2 output pin (PA8 for MCO1, PC9 for MCO2)
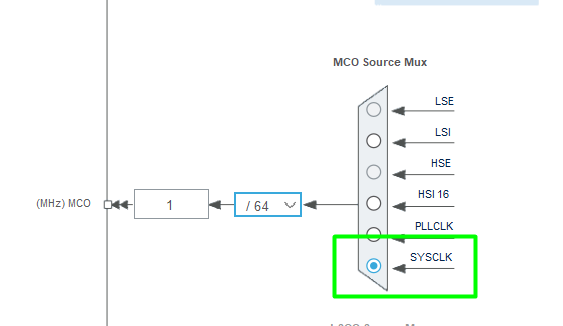
3. Select clock source for MCO: HSI, HSE, PLL, or SYSCLK
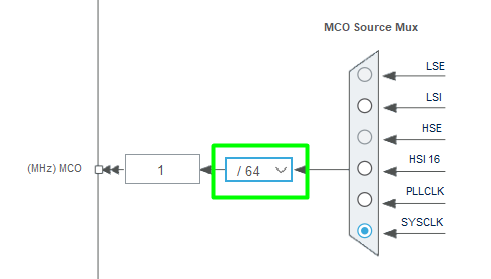
4. Set prescaler for MCO (optional) to divide frequency
5. Generate HAL code
5. HAL Example: MCO Configuration
void MX_RCC_MCO_Init(void)
{
// Output SYSCLK on MCO1 (PA8) with no division
HAL_RCC_MCOConfig(RCC_MCO1, RCC_MCO1SOURCE_PLLCLK, RCC_MCODIV_1);
// Optional: Output HSE or HSI instead
// HAL_RCC_MCOConfig(RCC_MCO1, RCC_MCO1SOURCE_HSE, RCC_MCODIV_2);
}
- RCC_MCO1SOURCE_PLLCLK selects the PLL clock as source
- RCC_MCODIV_1 sets no prescaler (1:1)
- PA8 can now be connected to oscilloscope or frequency counter
6. Hands-On Lab Example
- Configure PLL to generate 64 MHz SYSCLK
- Route PLL output to MCO1 (PA8)
- Observe frequency on oscilloscope: should read 64 MHz / MCO prescaler = 1 MHz
- Change MCO source to HSI or HSE and measure frequency changes
- Demonstrate clock tree impact on system behavior
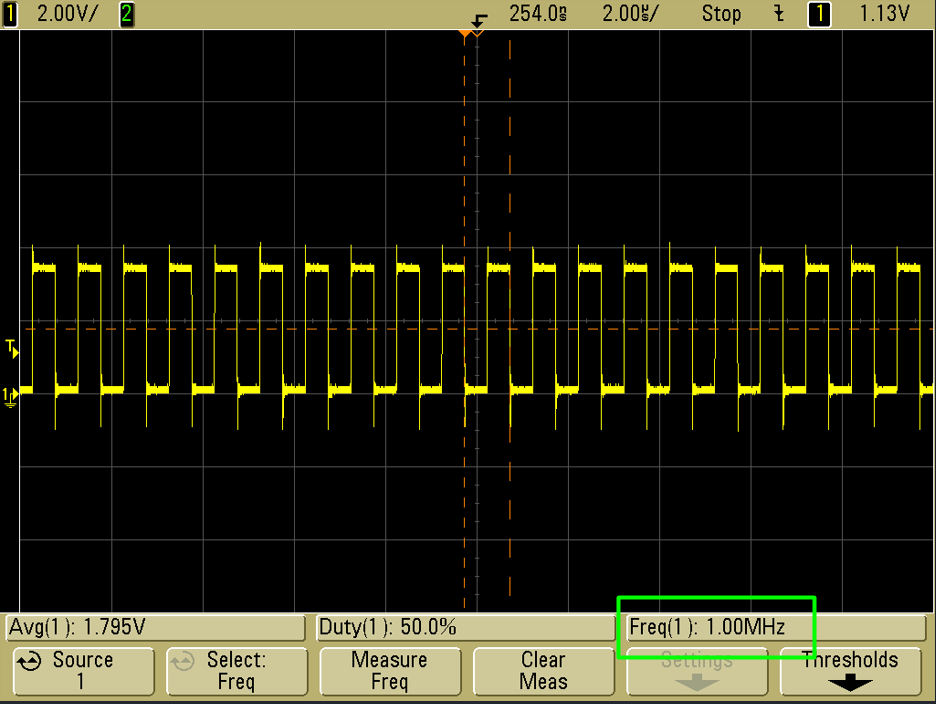
Tip: Adjust PLL multipliers or prescalers and observe MCO output for real-time validation
7. Practical Applications
- Debugging clock configuration issues
- Validating PLL, HSE, or HSI frequencies
- Measuring real system clock for peripherals
- Synchronizing external devices with MCU clock
8. Advantages
- Provides real-time clock measurement
- Useful for debugging and validation
- Helps understand RCC clock tree behavior
- Essential for timing-sensitive applications like DAC, ADC, and communication peripherals
9. Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| MCO pin output not visible | Pin not configured as alternate function | Set PA8/PC9 to AF mode in CubeMX |
| Frequency incorrect | PLL or prescaler misconfigured | Verify RCC clock tree and HAL_RCC_MCOConfig parameters |
| MCU unstable | SYSCLK too high for MCU specs | Adjust PLL multiplier/divider to within max SYSCLK |
| Oscilloscope shows noise | High-frequency interference | Use short probe ground lead or low-capacitance probe |