STM32 HAL Tutorial: Sending and Receiving Data via USART
Abstract
Learn how to configure UART/USART communication on STM32 using CubeMX and HAL drivers. Step-by-step guide to send and receive data with interrupts and DMA.
1. Introduction
In previous episodes, we learned about GPIOs, interrupts, and timers.
Now, it’s time to explore UART communication, one of the most widely used protocols in embedded systems for:
- Sending debug messages to a PC.
- Communicating with sensors or modules.
- Interfacing between multiple microcontrollers.
In this episode, you’ll learn:
- Configuring UART/USART in CubeMX.
- Sending data from STM32 to a PC.
- Receiving data using polling, interrupts, and DMA.

2. Prerequisites
- STM32 development board with USART pins exposed (TX/RX).
- STM32CubeIDE installed.
- USB-to-Serial converter (if board doesn’t have built-in USB).
- Basic knowledge of HAL GPIO and timers.
3. Configuring UART in CubeMX
Step 1 – Open Project
- Create a new project in STM32CubeMX.
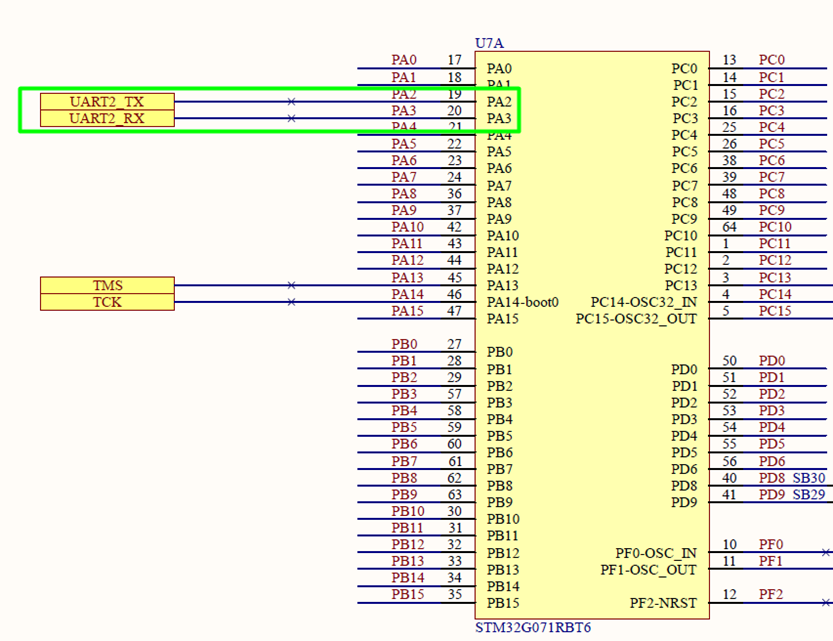
Step 2 – Enable USART Peripheral
- Go to Pinout & Configuration
- Select a UART peripheral (e.g., USART2).
- Assign pins for TX (transmit) and RX (receive).
Step 3 – Configure UART Parameters
- Click USART Configuration → Parameter Settings:
- Baud Rate: 115200 (common for debugging)
- Word Length: 8 bits
- Stop Bits: 1
- Parity: None
- Mode: TX + RX
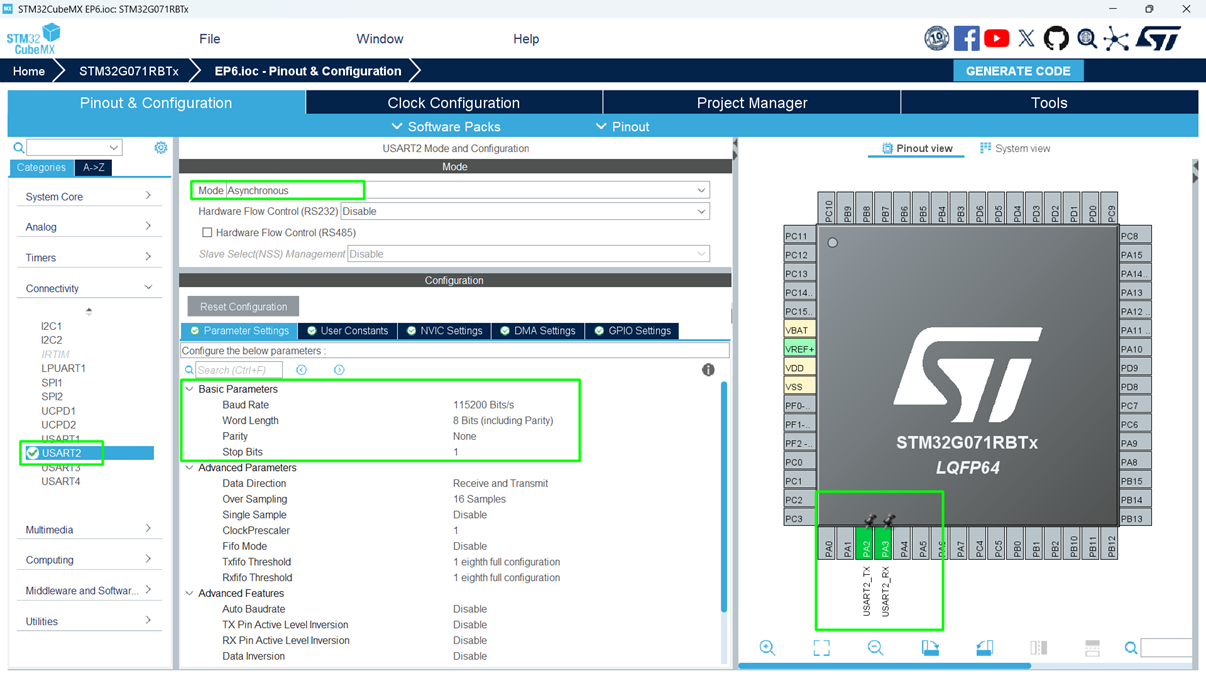
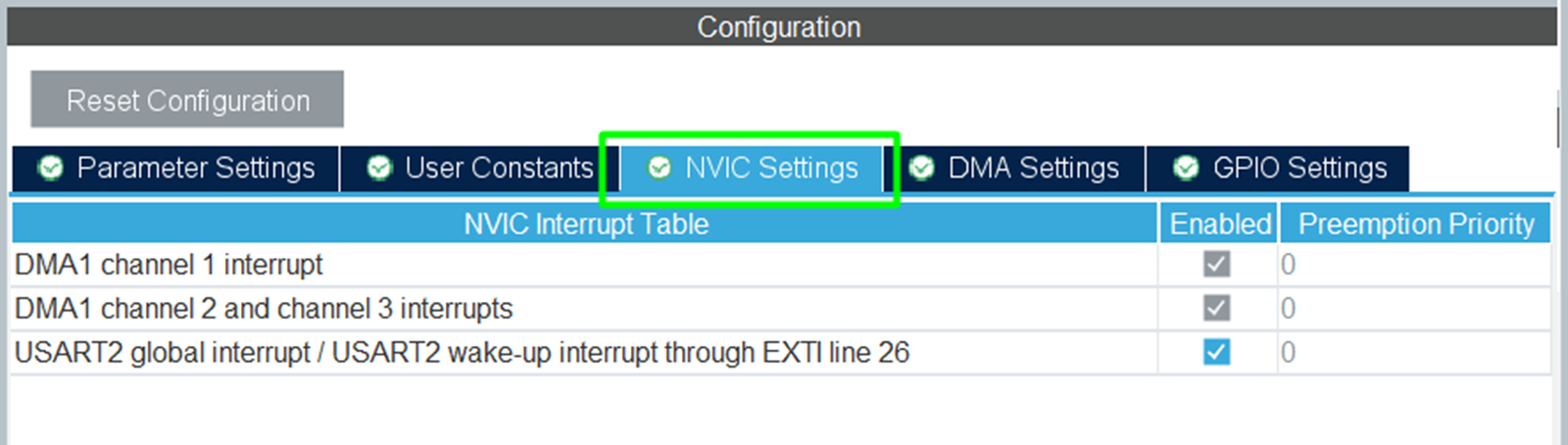
Step 4 – Enable NVIC Interrupt (Optional)
- For interrupt-based reception, enable USART global interrupt in NVIC.
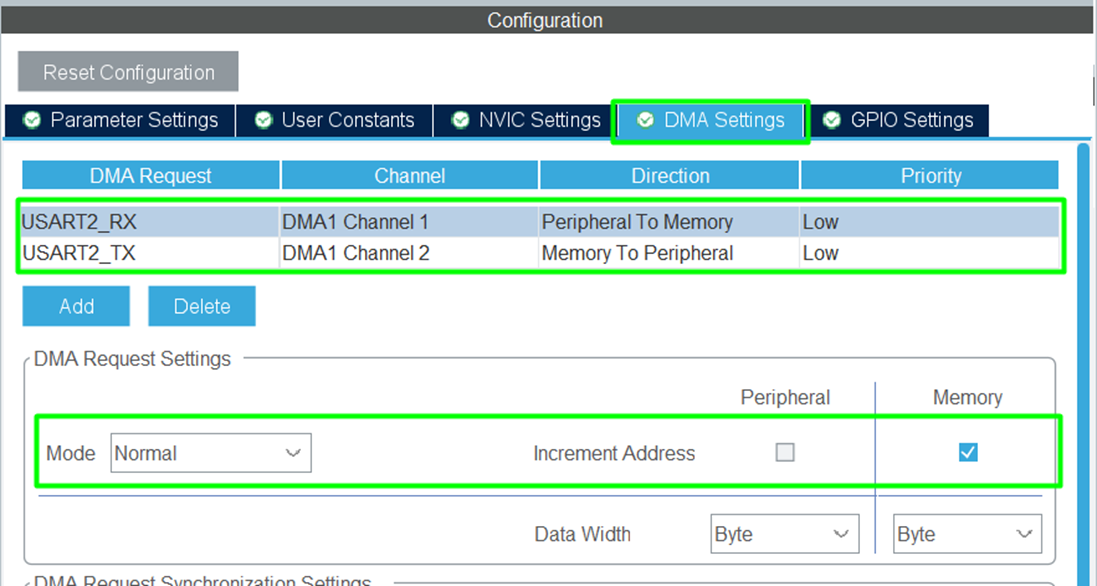
Step 5 – Enable DMA for Tx and Rx (Optional)
- For DMA-based reception, enable USART DMA Tx and Rx.
Step 6 – Generate Code
- Click Project → Generate Code to update HAL initialization.
4. Sending Data via UART
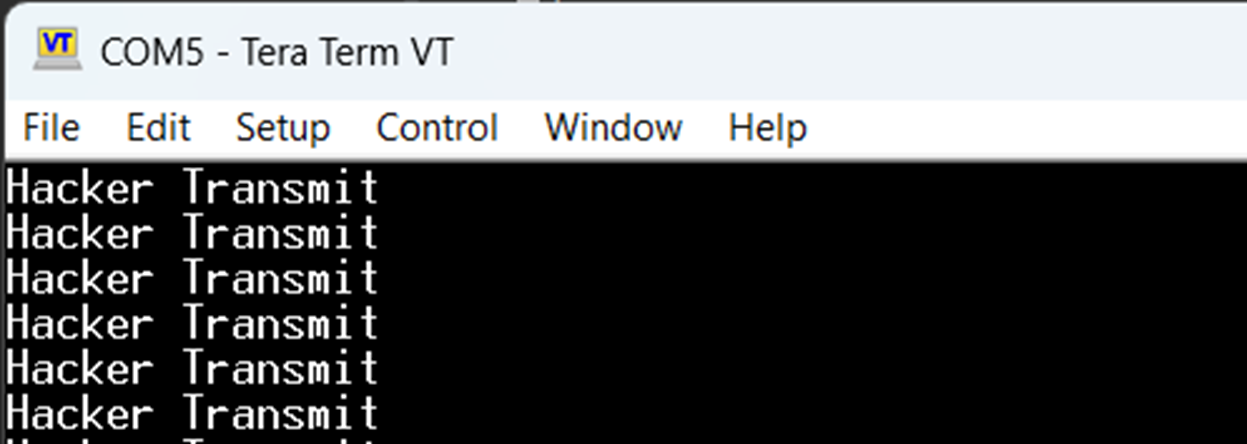
Open main.c and add the following code:
char msg[] = "Hacker Transmit\r\n";
int main(void)
{
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
while(1)
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t*)msg, strlen(msg), HAL_MAX_DELAY);
HAL_Delay(1000); // Send message every 1 second
}
}
Code Explanation
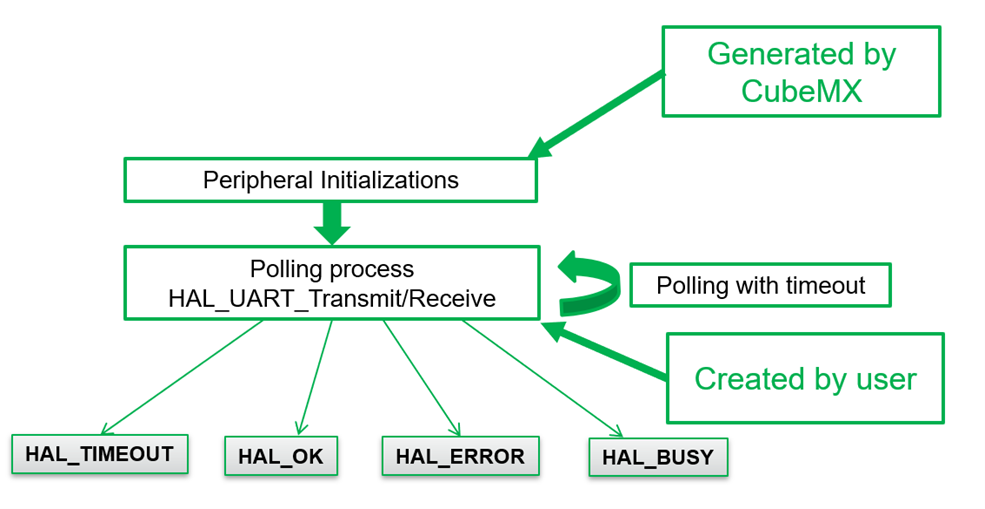
- HAL_UART_Transmit() sends data over UART.
- (uint8_t*)msg → Convert string to byte array.
- HAL_MAX_DELAY → Wait until transmission completes.
- HAL_Delay(1000) → Sends a message every 1 second.
5. Receiving Data via UART
Polling Method
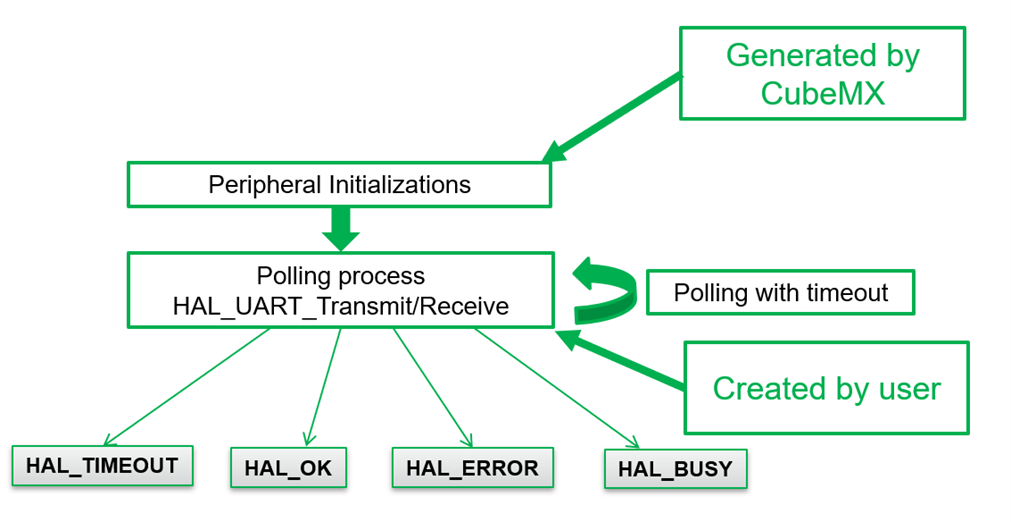
uint8_t received;
if(HAL_UART_Receive(&huart2, &received, 1, 1000) == HAL_OK)
{
// Process received byte
}
Interrupt Method
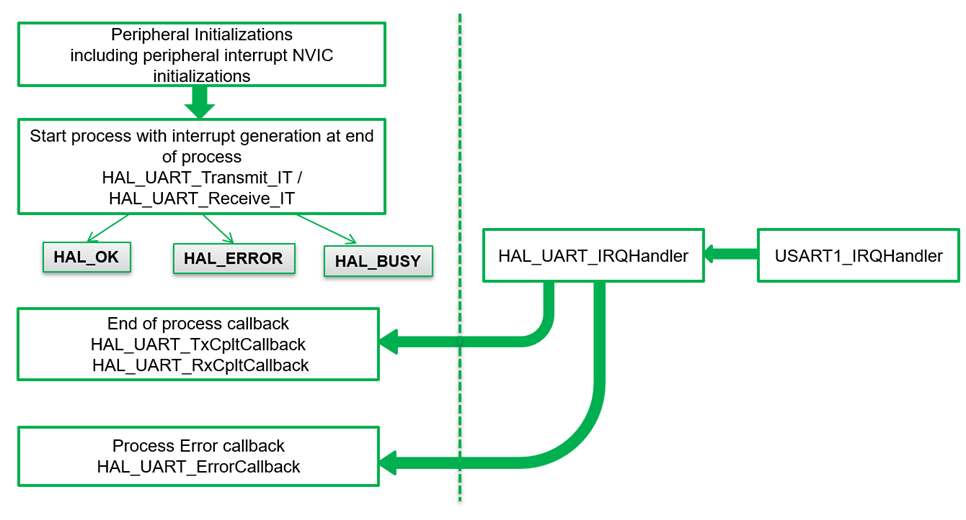
CubeMX generates a callback function:
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
if(huart->Instance == USART2)
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, &received_data, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY); // Echo back
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, &received_data, 1); // Re-enable interrupt
}
}
- Receives data without blocking the main loop.
- Ideal for responsive applications.
DMA Method
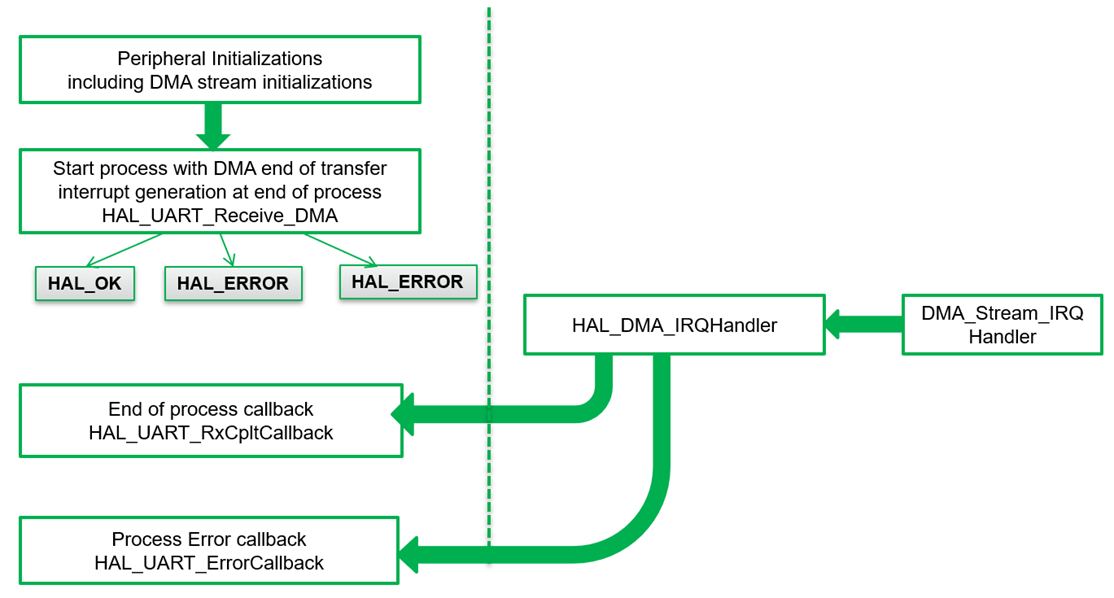
- Offloads data transfer to DMA controller.
- Useful for high-speed or large data streams.
- CubeMX can automatically configure USART + DMA for RX/TX.
6. Compiling and Running
- Build Project → Click hammer icon or press [Ctrl + B].
- Flash Project → Connect STM32 and run or enter in Debug Mode.
- Test Transmission → Open Serial Monitor; messages appear every second.
- Test Reception → Type characters; MCU can echo them back using interrupts or DMA.
7. Hands-On Lab Recap
You learned:
- How to configure UART/USART in CubeMX.
- How to transmit data to a PC using HAL.
- How to receive data using polling, interrupts, or DMA.
- How UART enables debugging and communication in STM32 projects.
8. Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No data received | Wrong TX/RX pins | Verify CubeMX pinout |
| Garbled characters | Baud rate mismatch | Set Serial Monitor to same baud (e.g., 115200) |
| Interrupt not firing | NVIC not enabled | Check CubeMX NVIC settings |
| Compilation error | HAL_UART functions missing | Regenerate CubeMX code |
9. What’s Next
In Episode 7, we’ll cover I²C communication:
- Connect STM32 to sensors or displays.
- Read and write data using HAL functions.
- Hands-on lab: Temperature sensor example.