STM32 HAL Tutorial: High-Precision Analog Measurements
Abstract
Learn how to implement ADC oversampling, averaging, and noise reduction on STM32 using HAL. Step-by-step guide for high-precision analog measurements.
1. Introduction
Real-world analog signals often contain noise or require higher resolution than the ADC’s native capabilities.
STM32 ADCs support techniques to improve measurement quality:
- Oversampling – Sampling multiple times per conversion to increase effective resolution
- Averaging – Computing the mean of multiple samples to reduce noise
- Noise reduction – Using hardware and software features to stabilize readings
By the end of this episode, you’ll be able to:
- Implement ADC oversampling and averaging
- Reduce measurement noise
- Achieve higher precision readings without external hardware
2. Prerequisites
- STM32 board with ADC
- STM32CubeIDE installed
- Knowledge of HAL, Interrupts and ADC
3. Oversampling Basics
- Concept: Take N samples and sum them → divide by N
- Effect: Each factor of 4 in oversampling increases resolution by 1 bit
- Formula: Vout =ΣNi=1ADCi /N
- MCU ADC oversampling can be hardware-assisted or manually in software
4. HAL Example: Software Oversampling
Reduces random noise and increases effective resolution:
#define OVERSAMPLE_COUNT 16
uint32_t adcSum = 0;
uint16_t adcValue;
for (int i = 0; i < OVERSAMPLE_COUNT; i++)
{
HAL_ADC_Start(&hadc1);
HAL_ADC_PollForConversion(&hadc1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);
adcSum += HAL_ADC_GetValue(&hadc1);
}
adcValue = adcSum / OVERSAMPLE_COUNT; // Averaged and oversampled value
5. Using ADC Hardware Oversampling (if supported)
- STM32H7, STM32G4, and STM32G0 MCUs support hardware oversampling
- Configure in CubeMX:
- Oversampling ratio (2x, 4x, 8x, …)
- Right shift (divide accumulated value automatically)
- Oversampling ratio (2x, 4x, 8x, …)
ADC_OversamplingTypeDef OversamplingConfig;
OversamplingConfig.Ratio = ADC_OVERSAMPLING_RATIO_16;
OversamplingConfig.RightBitShift = ADC_RIGHTBITSHIFT_4;
HAL_ADCEx_ConfigOversampling(&hadc1, &OversamplingConfig);
- ADC returns averaged and higher resolution value automatically
6. Noise Reduction Techniques
- Increase ADC sampling time → reduces input impedance mismatch noise
- Enable internal voltage reference (VREFINT) → improves stability
- Filter software data: moving average, exponential smoothing
- Use differential mode if supported for sensor signals
7. Hands-On Lab Example
1. Configure the selected analog channel
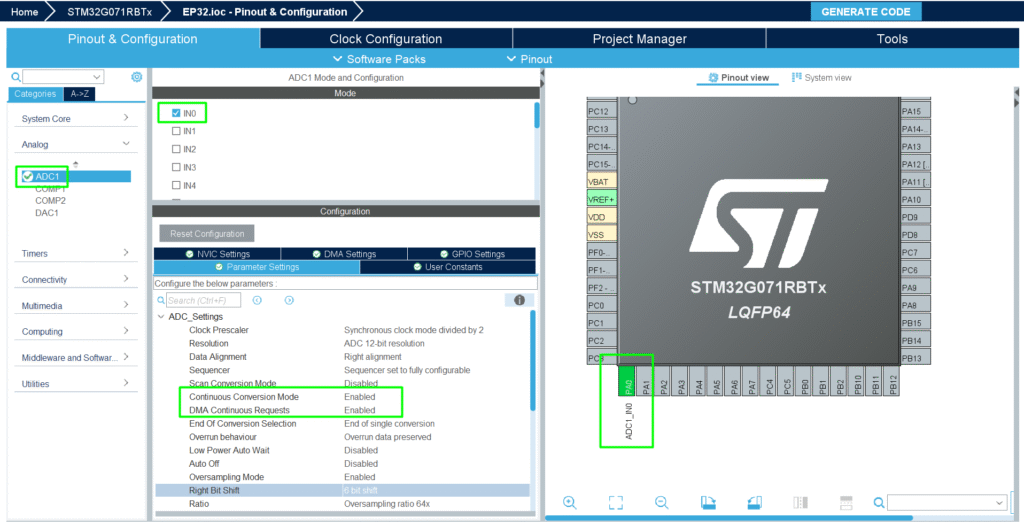
2. Configure ADC oversampling (hardware)
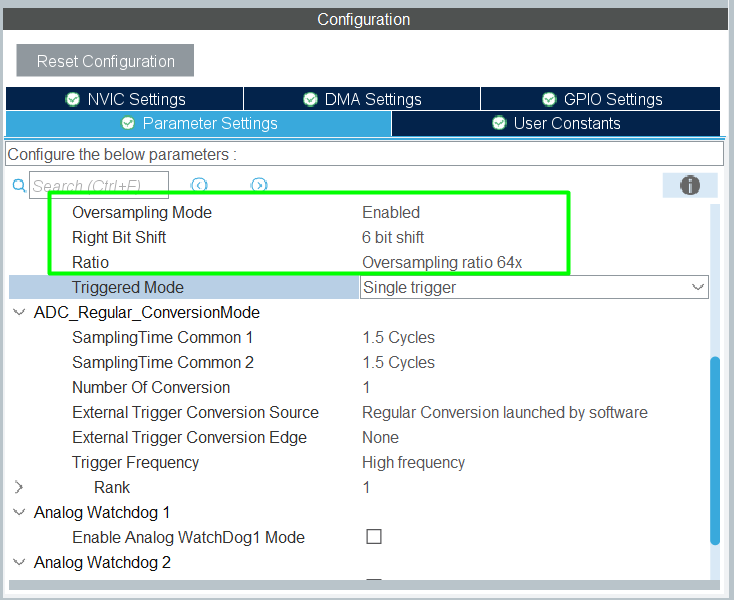
3. Configure the DMA
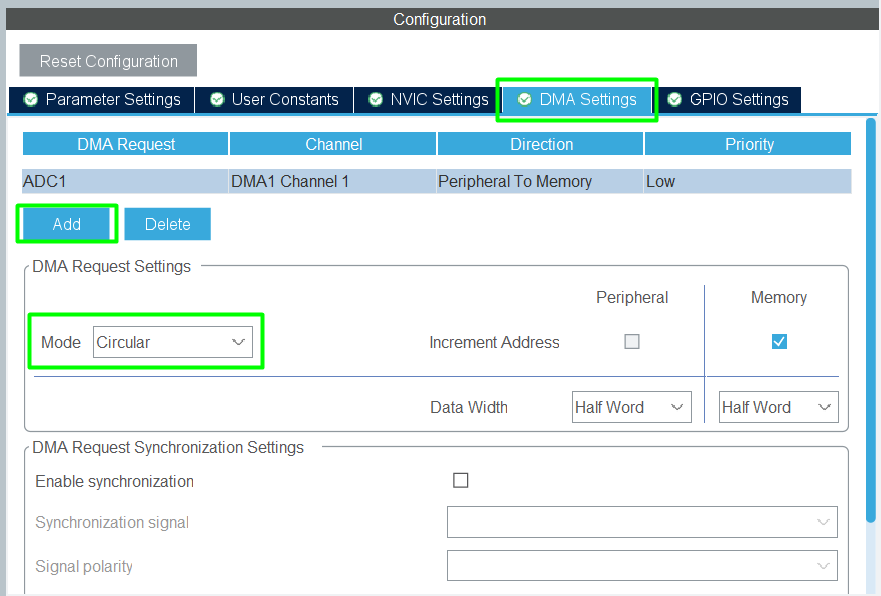
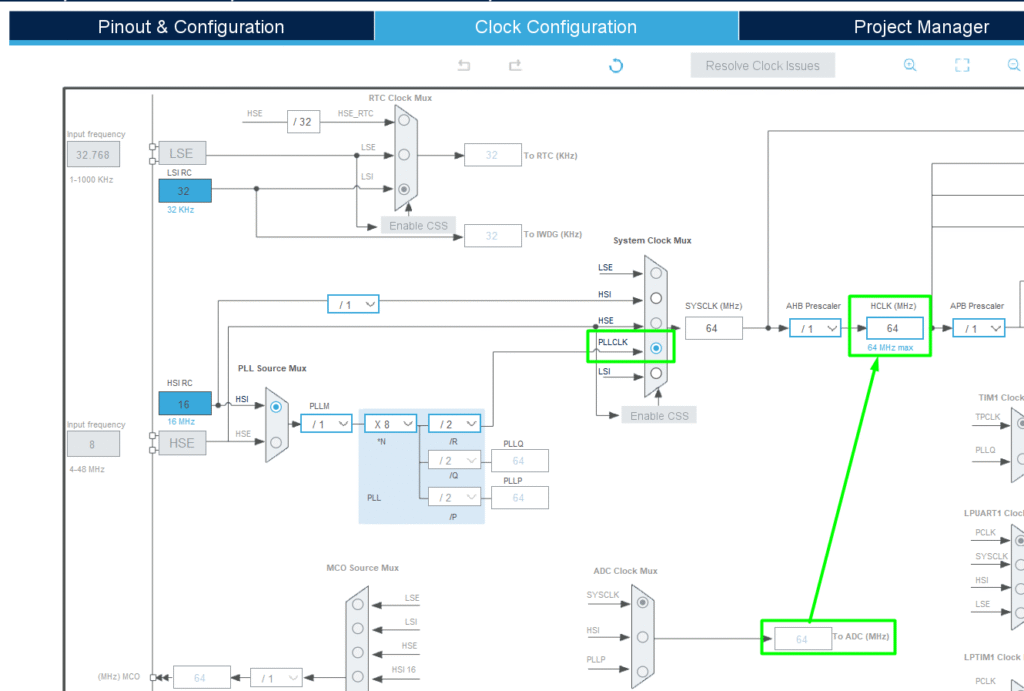
4. Configure the desired clock
5. Read multiple samples and compute average by hardware
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
uint16_t u16ADCBuff[16];
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_ADCEx_Calibration_Start(&hadc1);
HAL_ADC_Start_DMA(&hadc1, (uint32_t *) u16ADCBuff, 16);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
6. Compare noisy single reading vs oversampled averaged reading
a. Oversampling
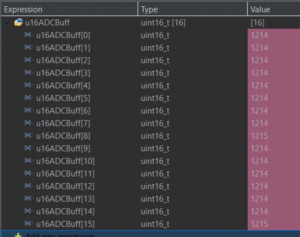
b. Single Read
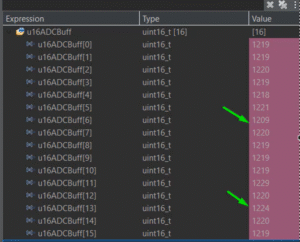
7. Optionally plot results on PC via UART
Tip: Combine hardware oversampling + DMA + low-pass software filtering for ultra-stable measurements
8. Advantages
- Improves effective resolution without external ADCs
- Reduces noise from sensors and analog circuits
- Compatible with DMA and low-power modes
- Ideal for precision measurement, sensor fusion, and control applications